
by Stemedix | Jun 26, 2023 | Degenerative Disc Disease
What is Degenerative Disc Disease?
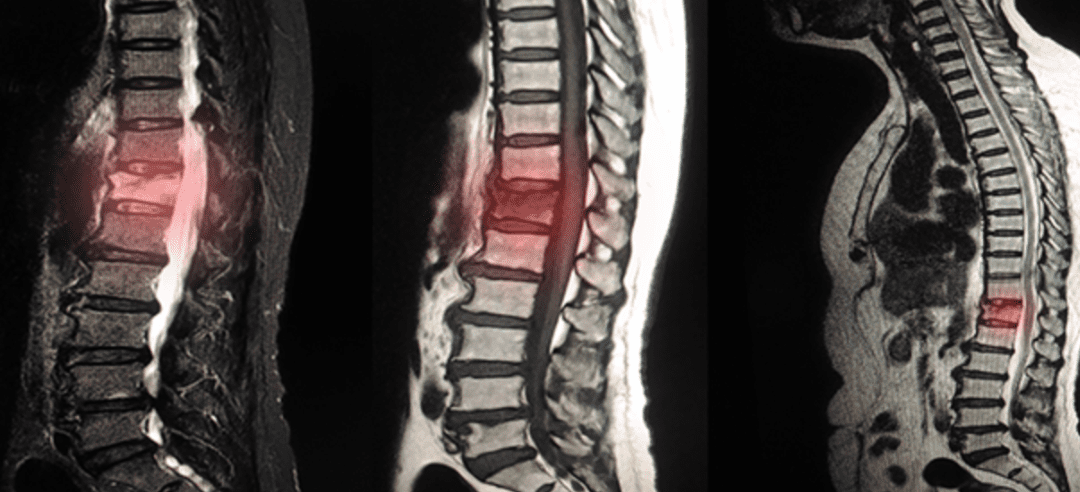
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a condition that refers to the gradual deterioration of the discs between the vertebrae of the spine. The discs are rubbery cushions that act as shock absorbers and provide flexibility to the spine. With age and wear and tear, these discs can degenerate, leading to various symptoms and changes in the spine. In this article, we will discuss the things to avoid with degenerative disc disease.
The primary cause of degenerative disc disease is the natural aging process. As we age, the discs lose their water content and become less flexible, resulting in decreased disc height and integrity. This degeneration can also be influenced by factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and repetitive stress on the spine.
The common symptoms of degenerative disc disease include back pain, neck pain, and radiating pain or numbness that can extend into the arms or legs. The pain may worsen with activities like bending, twisting, or sitting for prolonged periods. In some cases, the degenerated disc may impinge on nearby nerves, causing additional symptoms such as weakness or tingling sensations in the affected areas.
While degenerative disc disease is a natural part of the aging process, not everyone with disc degeneration experiences symptoms. The severity of symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Diagnosis of degenerative disc disease typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to assess the condition of the discs and rule out other possible causes of pain.
Who Do You See if You Think You Have Degenerative Disc Disease?
If you suspect that you have degenerative disc disease (DDD), it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in spine conditions. Here are some healthcare providers you can consider seeing for an evaluation and diagnosis:
Primary Care Physician (PCP): Start by scheduling an appointment with your primary care physician. They can assess your symptoms, perform a physical examination, and provide initial guidance. They may also refer you to a specialist for further evaluation if needed.
Orthopedic Surgeon: An orthopedic surgeon specializes in the musculoskeletal system, including conditions related to the spine. They can evaluate your symptoms, order appropriate diagnostic tests, and discuss treatment options ranging from conservative approaches to surgical interventions.
Neurologist: Neurologists are medical doctors who specialize in conditions related to the nervous system, including spine-related issues. They can evaluate your symptoms, perform neurological examinations, and order imaging tests to help diagnose degenerative disc disease. They can also provide recommendations for treatment and management.
Spine Specialist: A spine specialist, such as a physiatrist or a spine surgeon, focuses specifically on spine-related conditions. They have expertise in evaluating and treating degenerative disc disease. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation, recommend appropriate diagnostic tests, and develop a tailored treatment plan based on your specific needs.
Physical Therapist: Physical therapists can play a crucial role in managing degenerative disc disease. They can assess your condition, develop an exercise program to strengthen the muscles supporting your spine, and provide guidance on proper body mechanics and posture.
It is important to note that the availability of these specialists may vary depending on your location and healthcare system. In some cases, your primary care physician may provide sufficient guidance and refer you to the appropriate specialist if necessary. Seeking professional medical advice is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and to develop an effective treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
Things to Avoid with Degenerative Disc Disease
When living with degenerative disc disease, it is important to be mindful of certain activities and habits that can worsen your symptoms or potentially harm your spine.
Firstly, heavy lifting should be avoided as it places excessive strain on your discs. If lifting is necessary, remember to use proper techniques and ask for assistance when needed.
Prolonged sitting or standing should also be minimized, as both positions can place stress on your discs. Instead, try to alternate between sitting and standing and incorporate short breaks or walks throughout the day.
High-impact activities such as running, jumping, or contact sports should be avoided, as they can further deteriorate your discs. Opt for low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling, which are gentler on your spine. Repetitive activities such as bending, twisting, or lifting should be minimized or balanced with frequent breaks to reduce strain on your discs. A sedentary lifestyle weakens the supporting muscles of your spine, so engage in regular physical activity and exercises that promote spinal health.
Maintaining good posture is crucial; avoid slouching or hunching over, especially during extended periods of sitting or standing. Use ergonomic chairs or supportive cushions to help maintain proper alignment.
Smoking is detrimental to your spinal health, so it is advisable to quit smoking or avoid exposure to secondhand smoke.
Excess body weight adds strain to your spine and accelerates disc degeneration, so maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is essential.
Emotional stress and poor sleep can increase muscle tension and exacerbate pain associated with degenerative disc disease, so prioritize stress management techniques and ensure you get enough restful sleep.
It is always recommended to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and to develop a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
What are Treatment Options for Degenerative Disc Disease?
Traditional treatment options for degenerative disc disease aim to manage pain, improve function, and prevent further deterioration. Conservative measures include physical therapy, pain medications, hot or cold therapy, and lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy weight and adopting proper body mechanics. In more severe cases, when conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgical interventions such as spinal fusion or artificial disc replacement may be considered.
It’s important to note that degenerative disc disease is a chronic condition, and while traditional treatment can help manage symptoms, it may not reverse the underlying degeneration.
Regenerative Medicine for Degenerative Disc Disease
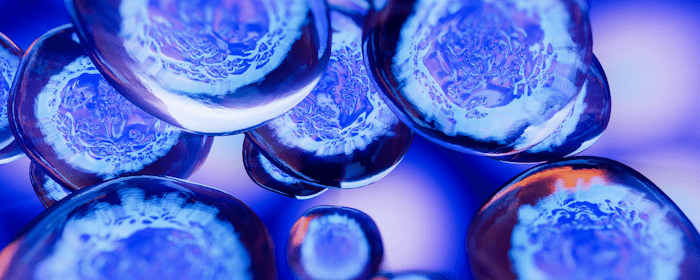
Regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy, is an emerging field that explores innovative treatments aimed at stimulating the body’s natural healing and regenerative processes.
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapy is a regenerative medicine approach that has gained attention for its potential in treating degenerative disc disease (DDD). MSCs are a type of adult stem cell that can differentiate into various cell types, including those found in intervertebral discs. These cells are administered to the targeted disc(s) to promote regeneration and repair.
Clinical studies and preliminary research on MSC therapy for DDD have shown promising results. Some potential benefits observed include decreased pain, improved disc hydration, increased disc height, and enhanced structural integrity. Consult with a qualified healthcare professional who specializes in regenerative medicine or spine conditions to discuss the potential benefits, risks, and availability of MSC therapy for degenerative disc disease. They can evaluate your specific case, and provide personalized recommendations based on your individual needs. To learn more about things to avoid with Degenerative Disc Disease, contact us today at Stemedix!

by admin | Jun 23, 2023 | Health Awareness, Alzheimer’s Disease
Caring for a loved one with Alzheimer’s disease can be emotionally challenging, especially when they experience agitation. Agitation is a common symptom of Alzheimer’s and can manifest as restlessness, pacing, aggression, or verbal outbursts. Witnessing your loved one in distress can be distressing for you as well. However, there are strategies and approaches you can employ to help manage and alleviate their agitation.
Here are some tips to assist you in supporting your loved one through this difficult time.
Identify triggers: Observe your loved one’s behavior and try to identify patterns or triggers that may lead to agitation. It could be certain activities, environments, or even specific times of the day. By recognizing these triggers, you can take steps to avoid or modify them, thereby reducing the likelihood of agitation.
Maintain a calm environment: Create a peaceful and soothing atmosphere for your loved one. Minimize noise, bright lights, and other sensory distractions that can contribute to agitation. Consider playing soft music or introducing familiar scents to promote relaxation.
Stick to a routine: Establishing a consistent daily routine can provide a sense of security and predictability for someone with Alzheimer’s. Help your loved one maintain regular sleep patterns, meals, and activities. Sudden changes or disruptions to their routine can increase agitation.
Practice effective communication: When interacting with your loved one, use simple and clear language. Speak slowly and calmly, maintaining eye contact. Avoid arguing or correcting them if they are confused or agitated. Instead, offer reassurance and validation of their feelings.
Engage in calming activities: Engaging your loved one in activities that they enjoy and find calming can help redirect their focus and reduce agitation. This could include listening to soothing music, doing puzzles, or going for a gentle walk together. Adjust the activities based on their abilities and interests.
Ensure physical comfort: Discomfort or pain can exacerbate agitation. Make sure your loved one is comfortable by addressing their physical needs. Check for hunger, thirst, or discomfort due to temperature. Regular exercise and massage can also promote relaxation and reduce restlessness.
Seek professional help: If agitation becomes persistent or unmanageable, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your loved one’s condition and suggest appropriate interventions or medications, if necessary. Additionally, support groups or counseling services can provide you with valuable guidance and emotional support throughout the caregiving journey.
Remember, caring for someone with Alzheimer’s requires patience and understanding. While you cannot eliminate agitation entirely, implementing these strategies can help alleviate your loved one’s distress and improve their quality of life. Don’t forget to prioritize self-care as well, as maintaining your own well-being is crucial in providing the best possible care for your loved one.

by admin | Jun 21, 2023 | Stem Cell Therapy, Regenerative Medicine, Stroke
Recent advances in medical accessibility, technology, and treatment have increased the average human life expectancy, while at the same time, increasing the risk for neurodegenerative diseases and other disorders – including stroke.
According to the CDC, nearly 800,000 people in the United States suffer a stroke each year, with 87% of these strokes being ischemic strokes. An ischemic stroke is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is reduced or interrupted. Without the ability to deliver oxygen or nutrients, brain cells begin to die in a matter of minutes.
Even when identified and treated early, the lasting, long-term effects associated with stroke result in economic and social costs for patients, their families, and society in general. As an example, the CDC estimates that stroke-related costs, including those associated with healthcare and missed days of work, exceed $50 billion dollars in the U.S. each year.
While medical research continues to search for ways to prevent stroke by addressing underlying causes, primary stroke treatment continues to focus on managing stroke progression while also treating related symptoms.
Recently regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy, along with rehabilitation therapy has been presented as an effective stroke treatment. In this review, Berlet, et al. explore the potential synergistic outcomes of stroke treatment observed when combining current advances in stem cell research with known stroke rehabilitation strategies. The authors also review research while considering the advantages and disadvantages of using the combination of stem cell transplantation and rehabilitation as a way to mitigate the devastating effects of stroke.
Combining stem cell treatment with rehabilitation therapy and outside strategies, such as an enriched environment (EE) may enhance functional stroke recovery and allow for an ideal long-term therapy for stroke patients. With the goal of enhanced brain plasticity, these therapies aim to introduce intrinsic or extrinsic stimuli to assist with the reorganization of the brain’s structure, functions, and connections.
The human brain has been demonstrated to be more plastic after experiencing an injury. With EE promoting improved stem cell survival and migration, and stem cell therapy creating the potential for an extended window of treatment, the combination is viewed as a potentially effective therapy when combined.
Preclinical experimentation has demonstrated stem cell therapies to be effective days after an ischemic stroke occurs, providing a very important window of time for critical stroke treatment to occur. While this is certainly promising information, the authors also point out that there has been a disappointing and frustrating disconnect between these preclinical findings and what is observed in clinical experimentation.
Considering this, the authors identify determining the optimal clinical stem cell route of administration, dosage, and timing as key areas of study to better understand – and maximize – the therapeutic potential of stem cells in the treatment of ischemic stroke.
While Berlet et al. calls for additional research into the ideal route of stem cell administration, type dosage, and timing to further confirm the efficacy of stem cell transplantation for the treatment of ischemic stroke, the authors conclude that the addition of stem cell therapy to rehabilitation has significant potential to create a conducive host microenvironment to facilitate the repair process.
Source: “Combination of Stem Cells and Rehabilitation Therapies for … – NCBI.” 6 Sep. 2021, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8468342/.

by Stemedix | Jun 19, 2023 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Athletic Injury
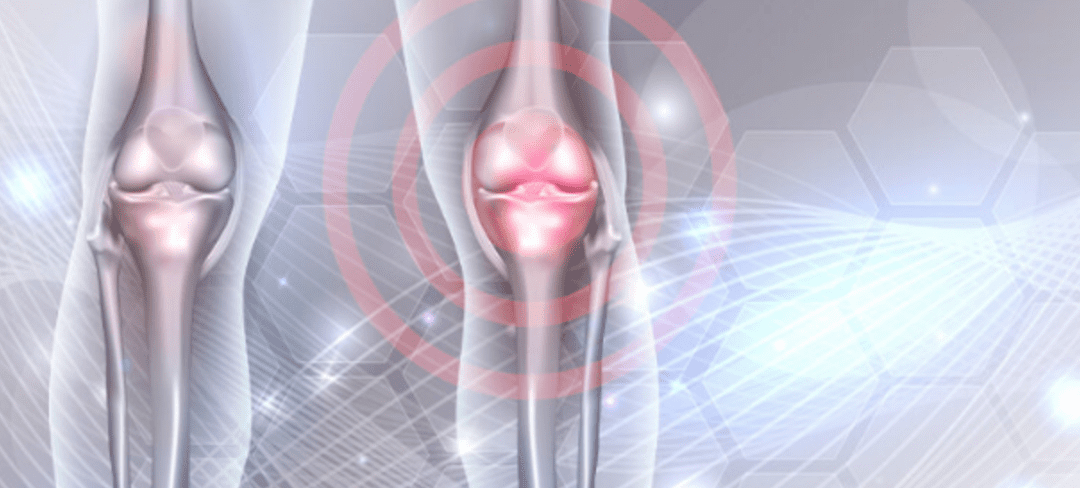
A very common question we get is ” How long does Stem Cell Therapy last for Knees? ” for those seeking this alternative treatment for the management of their knee pain. But first, we will discuss what can be behind the knee pain as a cause, who to seek a medical diagnosis, and what options a patient has.
What Can Cause Knee Pain?
Knee pain can have various causes, leading to discomfort and limitations in daily activities. One common cause is injuries, which can occur from sudden trauma or repetitive strain. Sprains, strains, ligament tears (like the anterior cruciate ligament or ACL tears), meniscus tears, fractures, or dislocations can result in knee pain.
Degenerative conditions like osteoarthritis often affect the knee joint. Over time, the protective cartilage on the ends of the bones wears down, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling. Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease, can also lead to knee pain due to joint inflammation.
Tendinitis, characterized by inflammation or irritation of the tendons around the knee, is typically caused by overuse or repetitive stress. Bursitis, another inflammatory condition, occurs when the small fluid-filled sacs (bursae) between bones, tendons, and muscles become inflamed.
Patellofemoral pain syndrome refers to pain around or behind the kneecap and is often caused by overuse, muscle imbalances, or improper tracking of the kneecap. IT band syndrome, on the other hand, arises from irritation or inflammation of the IT band along the outer thigh and can cause outer knee pain.
Conditions such as gout, marked by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, can lead to sudden and severe knee pain, redness, and swelling. Infections, though rare, can also cause knee pain, with symptoms including warmth, redness, and swelling.
Additional factors contributing to knee pain include ligamentous or muscular strains, bone tumors, obesity, poor biomechanics, or referred pain from other parts of the body.
If you are experiencing persistent or worsening knee pain, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis so to better help the treatment planning.
Who Do I See if I Have Knee Pain?
If you have knee pain, there are several healthcare professionals you can consult with for evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment. The appropriate healthcare provider may depend on your specific situation and the severity of your knee pain. Here are some specialists who commonly deal with knee-related issues:
Primary care physician (PCP): Your first step is often to see your primary care physician. They can assess your knee pain, perform a physical examination, and provide initial treatment or refer you to a specialist if needed.
Orthopedic specialist: Orthopedic doctors specialize in the musculoskeletal system and commonly treat knee pain and related conditions. They can diagnose the underlying cause of your knee pain, recommend imaging tests, if necessary (such as X-rays or MRI), and provide both nonsurgical and surgical treatment options.
Rheumatologist: If your knee pain is suspected to be related to inflammatory or autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, a rheumatologist can provide expertise in diagnosing and managing such conditions.
Sports medicine specialist: These specialists focus on injuries and conditions related to sports and physical activity. If your knee pain is sports-related or if you have an active lifestyle, a sports medicine specialist can help with diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation.
Physical therapist: Physical therapists can be involved in the treatment of knee pain, especially for rehabilitation and strengthening exercises. They can provide exercises, stretches, and techniques to improve knee function and reduce pain.
Pain management specialist: If your knee pain is chronic and not easily managed with conventional treatments, a pain management specialist can provide additional options such as medications, injections, or other interventional procedures to alleviate pain.
Are There Alternative Medicine Treatments for Helping with Knee Pain?
Yes, there are alternative medicine treatments that some individuals may consider for helping with knee pain. These alternative approaches focus on holistic and natural methods to address pain and promote overall well-being. While they may not be suitable or effective for everyone, some people find them helpful as complementary or adjunct therapies. Here are a few alternative medicine treatments that are sometimes used for knee pain:
Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. Acupuncture is believed to stimulate energy flow and promote pain relief and healing. Some people report reduced knee pain and improved function with acupuncture.
Herbal remedies: Certain herbs and botanicals are believed to have anti-inflammatory properties and can be used topically or taken orally to alleviate knee pain. Examples include turmeric, ginger, Boswellia, and willow bark. However, it’s essential to consult with a qualified herbalist or healthcare provider before using any herbal remedies, as they can interact with medications and have potential side effects.
Topical creams and ointments: Various topical preparations containing natural ingredients like arnica, menthol, capsaicin, or essential oils are available and can be applied to the knee to provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation.
Mind-body techniques: Practices such as meditation, mindfulness, yoga, and tai chi can help manage knee pain by promoting relaxation, reducing stress, improving flexibility, and enhancing body awareness. These techniques may also improve overall physical and mental well-being.
Physical therapies: Alternative physical therapies like chiropractic care, osteopathy, or naturopathy may incorporate manual techniques, stretching, manipulation, or mobilization to address knee pain. These approaches often aim to enhance joint mobility, improve alignment, and reduce pain.
Regenerative Medicine: Also known as stem cell therapy, this regenerative medicine utilizes mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for joint pain by promoting healing, repair, and regeneration of damaged joint tissues.
What is MSC Therapy for Knee Pain?
MSC (mesenchymal stem cell) therapy is a form of regenerative medicine that has gained attention as a potential treatment for knee pain and knee-related conditions. MSCs are multipotent cells that have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, including bone, cartilage, and fat cells. They also possess anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties. Most people ask the question of ” How long does Stem Cell Therapy for knees last? ” With MSC Therapy for Knee Pain in mind.
The goal of MSC therapy is to promote tissue regeneration, reduce inflammation, and potentially slow down the progression of conditions such as osteoarthritis. By injecting MSCs into the knee joint, it is believed that the cells can stimulate the repair of damaged tissues, enhance cartilage regeneration, and modulate the immune response, thereby reducing pain and improving function.If you are considering MSC therapy for knee pain, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who specializes in regenerative medicine. They can assess your specific situation, discuss the potential benefits and risks, and provide guidance on whether MSC therapy is appropriate for you as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Looking to inquire further about how long does stem cell therapy last for knees, contact us at Stemedix today.

by admin | Jun 16, 2023 | Health Awareness, Multiple Sclerosis
Living an active lifestyle is important for individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) as it can help manage symptoms, improve overall well-being, and maintain physical function.
Regular physical activity can help manage the symptoms associated with MS, such as fatigue, muscle weakness, spasticity, and balance issues. It has been shown to reduce fatigue and improve mood, leading to an overall enhanced sense of well-being. By engaging in regular exercise, individuals with MS can preserve and improve their physical function, including muscle strength, flexibility, and endurance.
What Are Some Activities?
Aerobic exercises, like walking or cycling, can improve cardiovascular fitness and reduce the risk of heart disease. Balance and coordination can be affected by MS, increasing the risk of falls. However, participating in activities that promote balance and coordination, such as yoga or tai chi, can enhance stability and reduce the risk of falls.
Regular physical activity also supports cognitive function, as it has been associated with improved memory, attention, and processing speed. Additionally, exercise can help manage weight, improve body composition, and promote a healthier overall body composition.
Include strength training exercises to improve muscle strength and tone. Work with a physical therapist or fitness professional to develop a safe and effective strength training program. Focus on major muscle groups, using resistance bands, free weights, or weight machines.
The social aspect of staying active is also beneficial, as it provides opportunities for social interaction, participation in group exercise classes, and joining support groups. This social connection can positively impact mental well-being and help individuals cope with the challenges of living with MS.
Be Sure to Stay Safe
Be adaptable as needed if certain exercises or movements are challenging due to MS symptoms. Adapt them to your abilities. For example, use assistive devices, modify the range of motion, or try seated exercises if necessary.
Start with realistic goals and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your activities. It is important that you listen to your body and know your limits. Pay attention to how your body feels during and after exercise. If you experience excessive fatigue, pain, or worsening of symptoms, adjust the intensity or take breaks as needed. It’s essential to strike a balance between staying active and allowing for proper rest and recovery.
Be sure to stay hydrated. Drink plenty of water before, during, and after exercise to stay hydrated, as MS can increase sensitivity to heat. Incorporate foods high in water content as an added benefit.
Ultimately, staying active can increase resilience, enhance the quality of life, and empower individuals to feel in control of their health and well-being. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any exercise regimen, preferably one experienced in working with MS patients. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific condition and abilities.



 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
