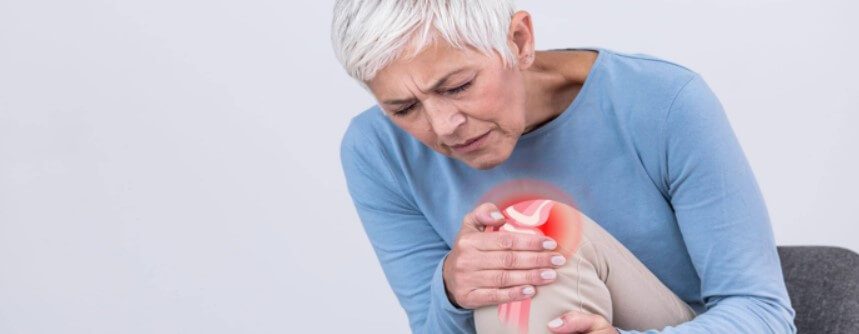
Ways to Get Osteoarthritis Pain Relief
Living with osteoarthritis pain can be debilitating. You might feel barred from activities you previously enjoyed. With osteoarthritis, everything feels more difficult, including playing with your grandkids, enjoying sports, and walking in nature.
Addressing osteoarthritis pain involves a combination of lifestyle changes, modern scientific therapies, and medications. Here are some of the ways you can get relief from the pain and discomfort osteoarthritis brings to your life.
The Root Cause of Osteoarthritis
Arthritis is an inflammatory joint condition that currently has no cure. If you have osteoarthritis, your body experiences cartilage degeneration. This means the spongy tissue that connects your bones together is starting to break down.
Bone Friction and Damage
When enough cartilage is lost, the friction of your bones rubbing together causes pain, inflammation, and discomfort. Your ligaments start to stretch in painful, unhealthy ways.
Osteoarthritis operates in two ways. Cartilage breakdown causes bone friction, which increases your pain levels. Bone friction also causes serious bone damage that worsens your pain.
Because of these stressors, osteoarthritis pain can be debilitating. This condition can be progressive, getting worse as your joints and ligaments become stressed due to lack of cartilage. If you get proper treatment, however, you may get rid of your symptoms altogether.
There are a few risk factors for developing osteoarthritis. With proper treatment, you can go into remission and experience far fewer painful symptoms.
Who Gets Osteoarthritis?
What causes your cartilage to break down in the first place? The answer is more complex than you might expect. Some people are more susceptible to joint and cartilage damage than others.
Older Adults
Age is a major risk factor for developing osteoarthritis. Patients who are 40 or older are more likely to develop this condition.
Throughout your life, your joints and connective tissues experience “wear and tear,” and the effects accumulate as you age. This can create problems with your cartilage’s structural integrity, eventually leading to osteoarthritis. It makes sense that aging adults experience higher rates of this inflammatory health condition.
People With Sudden Injuries
You may develop osteoarthritis if you’ve experienced a sports injury or sudden joint impact. Injuries can harm the cartilage that connects your joints, increasing your risk of developing this condition.
If you’re an older adult who played sports in your younger years, you may notice symptoms of osteoarthritis popping up as you age. Car crash victims and people with traumatic joint injuries are also vulnerable.
Obese Patients
Obesity raises your risk for this degenerative disorder. The more extra fat you carry, the more stress and pressure your joints experience. Over time, excess body weight can break down connective tissues in your knees, legs, and feet.
Since osteoarthritis is an inflammatory condition, being obese can exacerbate the symptoms. If you eat a poor diet full of processed foods and refined sugars, your body is more vulnerable to inflammation. These conditions make osteoarthritis symptoms even more debilitating.
How to Get Relief from Osteoarthritis Pain
The joint pain and discomfort that come with osteoarthritis can impair your daily life. If you like to be active and move around a lot, this disease may force you to change your lifestyle. Luckily, you have options when it comes to osteoarthritis pain relief.
From over-the-counter pain medications to natural holistic remedies, there’s no shortage of osteoarthritis pain relief. You can choose what works best with your personal preferences and lifestyle.
Pharmaceutical Treatments
Most physicians recommend over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs to manage osteoarthritis pain. If you have debilitating discomfort, some doctors will prescribe stronger pain medication. These treatments are usually intended for short-term use.
While medication covers up the pain you’re experiencing, it doesn’t solve the underlying problem. You likely won’t get long-term relief from medication alone.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell treatments for osteoarthritis may reduce inflammation and pain over time. This evidence-based therapy uses special “blank” cells to regenerate damaged tissues. Since osteoarthritis is a degenerative condition, stem cell therapy is a potentially effective solution to cartilage breakdown.
Stem cells come from the human body. These treatments are completely drug-free and use the natural powers of your body’s wound-healing process. Patients who seek stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis may notice significant improvements in their comfort levels after a few weeks.
Specialized Massage
Massages can help improve blood flow to the affected areas. As a result, massage therapy may be a good supplemental tool for relieving osteoarthritis pain.
Many people experience better mobility after a few massage therapy sessions. A massage therapist specializing in osteoarthritis pain relief can help you feel more comfortable and mobile in your daily life.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a holistic solution for joint pain osteoarthritis causes. Patients from different backgrounds and with various health problems have experienced pain relief from acupuncture. This therapy uses tiny needles to relax your muscles and redirect your brain’s pain signals.
Acupuncture should be used as a supplement to other types of therapy. It can provide short-term relief, but much like medication, it doesn’t treat the root cause of your osteoarthritis pain.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes offer effective, natural solutions to your daily discomfort. Nutrition, weight, sleep, and stress management all play large roles in osteoarthritis pain relief.
Your body needs the right nutrients to control inflammation and accelerate wound healing. You also need plenty of sleep and stress management to maintain a healthy body. Any or all of these factors can improve or worsen your osteoarthritis pain.
As a rule of thumb, you should prioritize:
- Healthy weight management
- Good nutrition
- Sleep quality and quantity
- Stress relief
- Gentle daily exercise
These lifestyle factors will all help your body recover from osteoarthritis attacks. You may be able to prevent the inflammation from getting worse by improving these areas of your life.
Experience Osteoarthritis Pain Relief to Enjoy Healthy Movement Again
You’re understandably ready to get back to doing what you love. Managing your osteoarthritis pain doesn’t have to take over your life. Live a healthy lifestyle as you consider different therapies and treatments to take the edge off of your joint pain.
Regenerative Medicine Options for Neuropathy Pain Management
Neuropathic pain is pain caused as part of a dysfunction in the nervous system, including the peripheral nerves, brain, and spinal cord. Often characterized by spontaneous pain occurring for no specific reason, neuropathic pain can range from mild to severe and is currently estimated to affect 150 million people in the United States. The risk of experiencing neuropathic pain is also much higher in those with preexisting medical conditions, especially diabetes.
Treating neuropathic pain has proven to be very challenging and, to date, most current medical treatments are designed to mitigate pain while not addressing the underlying cause of the pain.
Spinal reorganization and changes in the excitatory or inhibitory pathways controlling neuropathic pain development following peripheral nerve injury are correlated with altered gene expression. Considering this, Siniscalco, Rossi, and Maione review newer molecular methods, including gene therapy and delivery of biologic anti-nociceptive molecules, as potential therapeutic approaches for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
The authors also review the use of stem cell therapy as the potential to slow the progression of or even altogether block neuropathic pain. Stem cells have the ability to incorporate into the spinal cord, differentiate, and to improve locomotion recovery. Furthermore, and despite associated ethical concerns, human stem cells have demonstrated the ability to migrate to the injured area of the spinal cord and differentiate in order to promote axon regeneration and synapse regeneration as a way to alleviate neuropathic pain and improve motor behavior.
Further exploring stem cell therapy as a potential treatment for neuropathic pain, Siniscalco et al. point out that using genetically engineered stem cells expressing trophic factors appears to be a useful tool in relieving neuropathic pain. The authors hypothesize that the benefit brought by stem cells could be a result of their ability to deliver anti-nociceptive molecules close to the pain processing centers or site of injury and that the trophic factors provided by stem cells could, themselves, act as an anti-nociceptive drug.
Of the many various types of stem cells, the authors believe that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) demonstrate the potential for the best results in pain-care research. Found throughout the body, MSCs demonstrate a high expansion potential, genetic stability, and stable phenotype, and are easily collected and transported.
In addition, MSCs also are able to migrate to sites of tissue injury and demonstrate strong immunosuppressive properties and are able to differentiate into neurons and astrocytes. Animal models of neurological disorders have demonstrated that MSCs are able to improve neurological deficits and to promote neuronal network improvements.
Although the underlying mechanisms of how MSCs specifically address pain behavior are yet to be fully understood, their ability to migrate to injured tissue and mediate functional recovery suggests that MSCs could modulate pain generation after a neuropathic injury.
The authors conclude that neuropathic pain is a very complex disease that is very difficult to treat. While current treatment is designed to address the symptoms of pain, a treatment for the cause has yet to be developed. There are new molecular methods, including antisense strategy, gene therapy, and virus therapy currently being evaluated as potential therapeutic options to treat the underlying causes of pain.
Most recently, preliminary clinical evidence suggests that stem cell therapy could be the most effective long-term treatment for definitive relief of pain caused by neuropathic injury or disease.
Source: “Stem cell therapy for neuropathic pain treatment – PMC – NCBI.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3908122/.

10 Most Common Autoimmune Diseases
Your body is generally very good at telling what’s a foreign invader, like a virus or bacteria, and what’s not — but sometimes, it gets it wrong.
If you have an autoimmune disease, your immune system has begun to associate parts of your body, like your skin or joints, as foreign. When this occurs, the body releases antibodies that attack those healthy cells.
Essentially, your immune system overreacts. That’s what leads to autoimmune diseases. There are many of these kinds of illnesses, but some are much more common than others.
1. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Attacking Your Joints
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease in which your immune system attacks the joints throughout your body. It attacks the joints on both sides of your body and leads to uncontrolled inflammation that damages cartilage. The joints can begin to deform, and your bones can even erode.
You can experience symptoms like:
- Pain, stiffness, and swelling in joints
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Weakness
With rheumatoid arthritis, you can have periods of remission when you have few to no symptoms, but these are followed by flare-ups.
2. Type One Diabetes: Targeting Insulin-Producing Cells
Your pancreas produces a hormone called insulin, which regulates your blood sugar levels. If you have type one diabetes, your immune system attacks the cells in your pancreas that produce insulin. You can experience symptoms like:
- Extreme thirst
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Frequent urination
- Weight loss
- Vaginal yeast infections
- Slow healing of sores and cuts
Type one diabetes has a strong genetic component, and there may be certain environmental factors, like viruses or toxins, that can also trigger the disease if you have a predisposition.
3. Multiple Sclerosis: Damaging Myelin Sheaths
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease that damages the coating that surrounds nerve cells. These are called myelin sheaths, and if they’re damaged, the transmission speed of messages between your brain and your spinal cord can be delayed.
You can experience symptoms like:
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness
- Changes to your vision
- Loss of balance
- Mood changes
- Trouble with cognitive function
You can experience remission periods in which you may not have any symptoms.
4. Psoriasis: Leading Skin Cells to Multiple Too Quickly
Usually, skin cells grow and then die off and shed. Psoriasis causes cells to multiply too rapidly, leading to the formation of patches. People who have lighter skin tones can have patches that appear red with white plaque scales, while on darker skin tones, the patches can appear purple or dark brown with gray scales.
It can cause symptoms like:
- Raised areas of thick skin
- Rashes
- Flaky or scaly plaque
There are a few types of psoriasis, with some appearing in your skin folds and some even causing pus-filled bumps.
5. Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Swelling in the Intestinal Wall
Inflammatory bowel disease causes the lining of the intestinal wall to swell. Different parts of your gastrointestinal tract are affected depending on where the inflammation is located.
Symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Anemia
- Malnutrition
- Weight loss
- Rectal bleeding
- Fecal incontinence
One type of inflammatory bowel disease is Crohn’s disease, which can cause inflammation anywhere along the tract, from your mouth to your anus. Ulcerative colitis, however, affects the lining of the large intestine and rectum. Microscopic colitis causes inflammation that can only be seen via a microscope.
6. Lupus: Causing Inflammation Throughout Your Body
Lupus is an autoimmune disease that causes your immune system to attack your entire body. Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen glands
- Hair loss
- Fever
- Rashes
- Blood clots
- Confusion
There are a few types of lupus, including lupus that only affects your skin and medication-induced lupus.
7. Graves’ Disease: Overworking Your Thyroid
This type of immune disease attacks your thyroid gland, leading it to produce too many hormones. This can lead you to experience symptoms like:
- Fast heartbeat
- Unintentional weight loss
- Goiter
- Heat intolerance
Some people who have this condition can experience symptoms that affect the skin or eyes.
8. Addison’s Disease: Impacting the Adrenal Glands
Addison’s disease is a chronic condition in which your adrenal glands don’t produce enough cortisol and aldosterone. Cortisol is a hormone that helps your body respond to stress while also helping you maintain blood pressure, heart function, and more. Aldosterone is a hormone that controls your body’s sodium and potassium levels.
You can experience symptoms like:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Patches of dark skin
- Fatigue that gets progressively worse
- Loss of appetite
- Dehydration
Some people also experience low blood sugar levels with the disease.
9. Sjögren’s Disease: Causing Dry Eyes and Mouth
This illness occurs when your immune system attacks the glands that create moisture in your mouth, eyes, and other parts of your body. There is primary Sjögren’s disease, which occurs on its own, and secondary Sjögren’s disease, which happens when another condition triggers the disease.
You can experience symptoms like:
- Dry nose and frequent nosebleeds
- Vaginal dryness
- Dry and itchy eyes
- Dry throat
Some people also experience muscle pain, swollen lymph nodes, and even trouble swallowing.
10. Celiac Disease: Attacking the GI Tract
People who have Celiac disease can’t have gluten, which is a protein found in rye, wheat, and other grain products. If you have this disease, your immune system reacts to any gluten it finds in the small intestine, leading to inflammation. You can experience symptoms like:
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal bleeding
- Constipation
Because your immune system attacks your gut if you eat gluten, it doesn’t allow you to receive the nutrients you need. People may experience nutritional deficiencies that can cause many other symptoms.
Managing Autoimmune Diseases with Regenerative Medicine
Most autoimmune conditions can be managed. One of the most promising options, especially when combined with other treatments, is regenerative medicine.
Regenerative medicine options like stem cell therapy harness your body’s natural healing mechanisms. They can help reduce inflammation, which plays a huge role in most autoimmune diseases. With less inflammation, blood circulation improves, bringing more nutrients and oxygen to the affected areas.
To determine whether regenerative medicine is a good choice to help manage your autoimmune conditions, consult with your doctor.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Managing Spinal Cord Injuries
Nerve damage resulting from spinal cord injury (SCI) often leads to temporary or permanent loss of function and contributes to poor quality of life. Most common among males below 30 years of age, SCI recovery has been limited specifically as a result of the low growth capacity of neurons and a lack of nerve growth factors.
While current SCI treatment focuses on stabilizing the injured area and preventing secondary injury through a combination of surgery, pharmacological intervention, and rehabilitation, the success of treatment has been limited and unable to stimulate spinal cord regeneration.
Considering the limited success of confidential SCI treatments, several types of stem cells are currently being tested for the treatment of SCI, including mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) isolated from bone marrow (BMSCs), umbilical cord (UC-MSCs), and adipose tissue (ADSCs).
In this review, Liau et al. discuss the current status of MSC therapy for SCI, criteria to consider when applying MSC therapy, and review novel biological therapies that can be used together with MSC therapy to enhance its therapeutic potential.
Based on the results of clinical trials, the authors conclude that MSC therapy is beneficial for SCI patients. While not all patients responded to MSC therapy, the authors note that observed improvement varied from patient to patient. In addition to discrepancies attributed to patient variations, source of MSC, route of stem cell administration, timing of cell administration, number of cell administrations, number of cells administered, and cell preparation methods were also observed to affect the efficacy of therapy.
Despite the delayed progress in phase III trials, there are several new therapeutic treatment strategies that incorporate stem cell secretory product-based therapy, including stem cell secretome therapy, scaffold-based therapy, and immunotherapy. The authors indicate that all of these novel therapeutic approaches may be able to be used in combination with MSC therapy to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs by improving cell survival, migration, engraftment, and proliferation.
The authors conclude this review by summarizing that, to date, MSC therapy has been demonstrated to be safe but unable to improve neurological function for all treated patients. Despite the limited success of this therapy, other studies are currently underway in an effort to improve the delivery of MSCs and MSC-derived products by utilizing scaffolds or by combining them with immunotherapy to improve the efficacy of the treatment.
Source: “Treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cells – NCBI.” 22 Sep. 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7510077/.

 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
