
by admin | Jan 7, 2022 | Stem Cell Therapy, Kidney Disease, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research
Current estimates indicate that kidney disease currently affects over 37 million US adults and over 10% of the global population[1]. Characterized by gradual loss of function, kidney disease generally progresses over time and culminates in the inability to remove waste and excess fluid from the blood[2].
Often demonstrating little to no symptoms in its early stages, chronic kidney disease tends to demonstrate increasing and dangerous symptoms as the condition advances.
To date, treatment for chronic kidney disease has been centered around causal control as a way of slowing the progression of the condition. However, these therapeutic treatment efforts, including multidrug therapy, have demonstrated an inability to reverse the condition from progressing to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and requiring additional therapy, dialysis, or kidney transplantation.
Considering the high cost and disruption to normal life function associated with dialysis and the severe shortage of viable kidney donors, neither dialysis nor transplant has proven to be ideal or often recommended treatment strategies. As a result, there has been renewed interest in new and more effective therapeutic options to alleviate, cure, or prevent kidney disease and to improve a patient’s survival and quality of life.
Evaluating the numerous and growing therapeutic applications associated with stem cells’ ability for self-renewal, proliferation, and differentiation, Liu et al.’s review explores the potential benefits offered toward improving renal function and supporting structural repair in those afflicted with kidney disease.
Despite the promising benefits of using stem cells to kidney repair and disease treatment demonstrated through prior preclinical study, the authors point out that certain ethical issues regarding the origin of stem cells, and specifically embryonic stem cells (ESCs) need to be addressed and overcome before clinical application of SCs.
Regardless of the stated drawbacks, Liu et. al concludes that the existing evidence demonstrates that stem cell therapy appears to be a clinically viable alternative for kidney disease, specifically for restoring normal kidney function and for progressing understanding about tissue regeneration, drug screening, and disease modeling.
Although stem cells demonstrate promise in this regard and while the immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) appear to make them the most promising SC for treating kidney disease, the authors also point out that further research is needed before definitively concluding which source of SC is best suited for this application.
As a result of this review, and in an effort to realize these findings into clinical applications in the future, the authors call for larger rigorously designed clinical trials to further assist in determining the clinical efficacy of SC therapy in kidney disease – including the appropriate selection of cell types, number of SCs required, and the appropriate route of administration.
Source: “Stem cells: a potential treatment option for kidney diseases.” 25 Jun. 2020, https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-020-01751-2.
[1] “Chronic Kidney Disease Basics – CDC.” https://www.cdc.gov/kidneydisease/basics.html.
[2] “Chronic kidney disease – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic.” 3 Sep. 2021, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chronic-kidney-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354521.

by admin | Dec 31, 2021 | Stem Cell Therapy, Diabetes, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research
According to recent data from the CDC, an estimated 30 million Americans currently have type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and another 88 million are considered to be prediabetic[1].
Occurring most often as a result of being overweight and/or sedimentary and often resulting in severe kidney, heart, or vision issues, T2DM has demonstrated to be difficult to treat, often resulting in life-long insulin therapy as the primary method of treatment.
Considering the negative impacts associated with insulin treatment, and T2DM in general, Liu, et al.’s research explores the potential of specific mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the treatment of the condition.
Recently, stem cell therapy has been shown to be beneficial in improving glycemic control and beta function. Building off of these findings, Liu, et. al designed this study to specifically examine the efficacy and safety of Wharton’s Jelly mesenchymal stem cells transplantation (WJ-MSC) as a therapeutic option for those with T2DM.
The authors’ single-center phase I/II study involved observing 22 patients with T2DM for 12 months after receiving two injections of WJ-MSC (one intravenously and one intrapancreatic endovascularly). Over the course of the 12-month observation period, the participants were monitored with primary endpoints observed including changes in the levels of glycated hemoglobin and C-peptide and secondary endpoints including insulin dosage, fasting blood glucose, post-meal blood glucose, inflammatory markers, and T lymphocyte counts.
At the conclusion of this study, Liu et al. found that both glycated hemoglobin and fasting glucose levels demonstrated a progressive decline after WJ-MSC transplantation and over the course of the 12-month follow-up period, the suggested potential of long-lasting effects of the WJ-MSC treatment. Researchers also observed a general improvement in fasting C-peptide levels. Secondary endpoint observations over the course of the 12-month follow-up included improved beta-cell function and reduced markers of systemic inflammation and T lymphocyte counts.
While there were no significant adverse observed effects associated with either of the WJ-MSC injections, the authors did note isolated and separate incidences of mild fever, nausea, and headache in a very small number of participants – all of which spontaneously resolved within a week of onset. The authors also noted a temporary decrease in levels of C-peptide and beta-cell function one month after treatment, possibly related to the intrapancreatic endovascular injection. As a result of these observations, the authors call for further investigation of the safety of intrapancreatic endovascular delivery of WJ-MSC.
As a result of this research, Liu et al. concluded that their findings suggest the possible therapeutic potential of WJ-MSC transplantation for treatment of T2DM and specifically with improved beta-cell function, systemic inflammation, and immunological regulation. The authors also call for further large-scale placebo-controlled clinical studies to fully understand the safety and efficacy of WJ-MSCs in the treatment of T2DM. Source: “PMC – NCBI.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4055092/
[1] “Type 2 Diabetes | CDC.” https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/basics/type2.html. Accessed 22 Jan. 2022.

by admin | Dec 10, 2021 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Articular cartilage is the smooth, white cartilage that covers the ends of the bone in diarthrodial joints. Essential for fluid and pain-free movement, articular cartilage protects the bones by reducing friction and absorbing shock.
However, articular cartilage is also subject to damage and injury as a result of normal wear and tear or as a result of a number of conditions, including osteoarthritis (OA), osteonecrosis, and osteochondritis. Articular cartilage has been found to have a weak capacity for self-repair, mostly a result of having no blood, lymphatic, or nerve supply.
Until recently, the primary option for treatment of joint cartilage defects, including damage to articular cartilage, involved a series of invasive marrow simulating techniques, including microfracture, Pridie drilling, and abrasion arthroplasty which generally produced inferior results.
The search for alternative and more effective treatment options for damaged joint cartilage has recently led scientists to identify mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) as an appropriate cellular material for repair of joint cartilage, and specifically for articular cartilage.
As part of this review, authors Eslaminejad and Poor examine and identify the past attempts to use MSCs as a way to cure articular cartilage defects occurring as a result of OA, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and trauma. In addition, the authors further discuss the specific characteristics that led scientists to conclude MSCs to be an appropriate cell candidate for regenerating articular cartilage, including their inherent chondrogenic property, ease of availability, cell homing potential, and immunomodulatory function.
MSCs demonstrate the ability for long-term self-renewal and the capacity to differentiate along multiple cell lineages – including cartilage cells. While bone marrow has been found to possess low numbers of MSCs, the cells have been easily multiplied through standard lab-based culture techniques. In addition, MSCs are considered readily available cells for application in regenerative medicine, thanks in large part to their availability from a number of sources in the body, including adipose tissue, synovial membrane, and skeletal muscle.
Among the most compelling reasons for MSCs being considered appropriate for the repair of articular cartilage is their homing potential. Specifically, the homing potential of MSCs is thought to help repair damaged cartilage by differentiating into tissue cells to restore function and by secreting a number of bioactive factors to create a repair environment with anti-apoptotic effects, immunoregulatory function, and stimulation of endothelial progenitor cell proliferation.
While using MSCs to repair damaged articular cartilage appears to have tremendous potential, the treatment is not without potential drawbacks or concerns. Among the most pressing of these concerns is that MSCs-regenerated cartilage is potentially too thin to resemble mature cartilage and hypertrophy resulting from MSC-regeneration could lead to ossification of cartilage tissue.
As such, there have been several recent attempts to evaluate the potential of using MSCs to regenerate articular cartilage in both animals and humans, with all demonstrating some degree of enhanced healing and repair by using MSCs as treatment.
The authors conclude that while using MSCs in the repair of damaged articular cartilage appears to have tremendous potential for long-term clinical success, they also call for further research into a number of areas, including improving the quality of repair tissue formed following MSC transplantation, enriching the cell population for chondrogenic cells, and further study into developing a safe and highly efficient gene delivery system for MSCs used in the regeneration and repair of articular cartilage.
Source: “Mesenchymal stem cells as a potent cell source for articular … – NCBI.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4131275/.

by admin | Dec 3, 2021 | Adipose, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, PRP, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, affecting more than 900 million people around the world. Developing when the cartilage that protects your bones wears down, osteoarthritis (OA) most commonly affects the joints of the hand, hips, spine, and knees[1].
While current treatment for OA and related joint damage is focused primarily on managing pain and minimizing further damage, function, and quality of life issues, no preventative therapeutic treatment currently exists for preventing or rehabilitating the condition.
Recently, stem cell therapy has been found to be an efficient therapeutic approach for treating degenerative joint conditions, including OA. Specifically, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), from adipose cells have been demonstrated to be the most promising type of stem cell for treating osteoarthritis.
In this study, Bui et al. studied the outcomes of applying MSCs harvested from adipose tissue in an effort to evaluate the therapeutic potential when transplanted in patients with grade II and III osteoarthritis.
Building on the findings of previously published studies, the authors specifically evaluated the in vitro and animal model effects of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells (ADSC).
Previous studies have demonstrated that PRP treatment of ADSCs promotes differentiation and proliferation into chondrogenic cells which resulted in improved healing of articular cartilage when ADSCs were pretreated with PRP. An additional study demonstrated the effects of PRP on the non-expanded stromal vascular fraction (SVF) in cartilage injury observed in an animal model, demonstrating significant regeneration of cartilage.
The aim of this clinical trial was to evaluate the efficiency and related side effects of non-expanded SVF when combined with PRP in treating OA grade II or III.
At the conclusion of Bui et al.’s study, patients demonstrated significant improvements in key measures, including improved joint function, decreased pain score, and improved gradual and consistent improvement observed in pre and post observations as measured by the Lysholm score.
As further evidence of the success associated with a therapeutic treatment combination of ADSC and PRP, post-treatment MRIs demonstrated cartilage regeneration and thicker layers of cartilage at the injured site after 6 months of treatment. In addition, all participating patients reported reduced pain levels after 3 months and 71% of patients demonstrated the ability to climb and descend stairs after 3 months. None of the patients participating in this study demonstrated infection, tumor formation, or any other side effect or complication as a result of this procedure.
As a result of their findings in this study, Bui et al. conclude that this therapeutic treatment method was successful in reducing pain, regenerating cartilage, and improving the quality of life for patients who participated. However, considering the small size of this study, the authors call for additional and larger-scale studies to confirm the potential for this promising, minimally invasive stem cell therapy for patients with osteoporosis.
Source: “Symptomatic knee osteoarthritis treatment using autologous adipose ….” 5 Oct. 2016, http://www.bmrat.org/index.php/BMRAT/article/view/11.
[1] “Osteoarthritis – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic.” 16 Jun. 2021, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/osteoarthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20351925.

by admin | Nov 26, 2021 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
When it comes to their potential for biomedical applications, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) continue to garner support and attention from the global scientific community. Isolated from a variety of sources, including bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue, MSCs demonstrate multipotent differentiation in vitro. In other words, they are tissues that are able to develop into more than one type of cell.
Considering MSCs ability to expand into osteogenic, chondrogenic, adipogenic, and myogenic cells for the purposes of repair and recovery, they continue to attract attention for treating a wide variety of conditions, including inflammatory lung and musculoskeletal disorders, multiple sclerosis (MS), and Crohn’s disease (CD).
As part of this review, Markov et al. provide a brief overview of MSC sources, migration process, and unique immunomodulatory attribute’s mechanisms while also focusing on the current findings pertaining to the immunoregulatory plasticity of MSCs and how that contributes to the regulation of immune response to elicit the desired therapeutic outcomes in patients suffering from immune-mediated/immune-dysregulating diseases.
Interestingly, the ability of MSCs to exhibit anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties has proven beneficial in clinical trials exploring therapeutic treatments of a number of immune-mediated disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and MS. Specifically, the findings of these clinical trials provide evidence that MSCs replace injured tissues while also serving as a source of growth factors and regenerative molecules. These findings also demonstrate that specific differential molecular mechanisms, when correctly identified, appear to be able to adjust the potential of MSCs in the regeneration of damaged tissue.
This review also explores the immunomodulatory properties of MSCs. Specifically, MSCs have been found to modify immunological reactions in several ways, including T cell suppression and induction of macrophages shift from M1 to M2, making MSCs an emerging therapeutic treatment option to a number of immune-mediated disorders including systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), MS, OA, RA, and CD.
Despite the observed benefits of MSCs in treating these immune-mediated disorders, the authors call for additional large-scale studies over prolonged periods of evaluation before fully utilizing MSCs in clinical applications.
Given their ability to differentiate into a wide variety of cells, their immunomodulatory competence, and lower ethical concerns, Markov et al. conclude that MSCs have good reason to be considered a viable therapeutic option for the treatment of a wide range of immune-mediated disorders.
While animal studies continue to provide evidence of the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of administration of MSCs in immunological disorder, the authors point out that potential of MSCs have not yet been fully realized through human clinical outcomes. Considering this, the authors call for further investigation and study to better understand how recruiting MSCs can improve migration and homing following transplantation.
Finally, the authors point out that enriching MSC culture, choosing appropriate induction factors, and exploring new ways to promote MSCs homing post-transplantation when accompanied by further exploration of optimal MSC dose and route will further improve therapeutic outcomes in patients with immune-mediated diseases.
Source: (2021, March 18). Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells as a valuable source for the … – NCBI. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7971361/

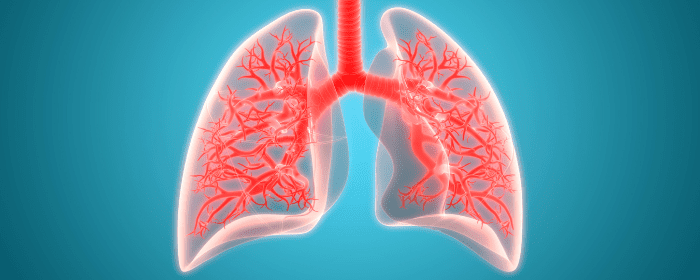
by admin | Nov 12, 2021 | Stem Cell Therapy, COPD, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research
Characterized by chronic inflammation that obstructs normal airflow from the lungs, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) affects an estimated 65 million people and remains the third leading cause of death worldwide. Caused by prolonged exposure to gasses or other harmful particulates, and especially cigarette smoke, COPD is typically characterized by breathing difficulty, cough, mucus (sputum) production, and wheezing[1].
While there are many different forms of COPD, the two most common are emphysema and chronic bronchitis; unfortunately, these two often occur simultaneously and significantly exacerbate the effects of COPD. With the number of people living with COPD expected to increase by 30% over the next decade, the disease is projected to remain among the leading causes of preventable illnesses and deaths for the foreseeable future.
There isn’t a known treatment or cure for COPD, rather a series of physical and chemical treatments designed to ease symptoms and slow progression of the disease; some current treatment includes bronchodilators, oral and inhaled steroids, antibiotics, oxygen therapy, and surgeries including lung transplantation and bullectomy. To date, these treatments have demonstrated limited success and are often associated with several severe adverse effects.
Recent research has shown mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) to be an effective therapeutic option for treating inflammation and autoimmune diseases, making them a promising therapeutic treatment option for COPD.
In this pilot clinical study, Le Thi Bich et al. evaluated the safety and efficacy of umbilical cord-derived (UC) MSCs for treating COPD. This pilot clinical study included participants who were 40-80 years old and diagnosed with moderate to severe COPD (stage C or D per the Global Initiative for Chronic Lung Disease). Using UC-MSCs cultured and expanded using the UC-SCI technology, Le Thi Bich et al. administered MSCs intravenously to participants as an intervention for assessment of therapeutic treatment for COPD.
After administering UC-MSCs on day 0, participants were evaluated for safety and efficacy at months 1, 3, and 6. At the end of month 6, researchers concluded that UC-MSC transplantation significantly improved some important outcomes of COPD, including mMCR, CAT, and number of exacerbations. While not statistically significant, the authors credit these improvements to an observed downregulation in inflammation.
While there have been several studies evaluating the potential of MSCs as therapies for several diseases, Le Thi Bich et al. ‘s study is the first clinical trial to use US-MSCs as a treatment for COPD.
The authors conclude that the UC-MSC transplantation occurring in this pilot study significantly improved the quality of life and clinical conditions of COPD patients, most likely a result of the strong immunomodulation capacity of the UC-MSCs – especially when compared to findings of other studies using bone-marrow MSCs.
The authors also conclude that the systemic administration of UC-SC appears safe and, although treatment efficacy was not significantly different between those with different stages of COPD, those with stage D COPD did exhibit stronger medical response after UC-MSC transplantation than the medical response observed in patients with stage C COPD.
The observed results of Le Thi Bich’s pilot study provide an important and significant basis for further clinical study of the potential of MSCs in patients with COPD.
Source: “Allogeneic umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell … – NCBI.” 13 Feb. 2020, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7020576/.
[1] “COPD – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic.” 15 Apr. 2020, https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/copd/symptoms-causes/syc-20353679. Accessed 1 Dec. 2021.

 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
