
by admin | Aug 4, 2022 | Health Awareness
Candida is a yeast, which is also a type of fungus, that normally lives on the skin and in areas of the body, including the mouth, throat, vagina, and digestive system. However, in cases where candida grows out of control or in areas of the body where it shouldn’t be present, it can form a fungal infection called candidiasis or Candida albicans.
Candida albicans causes conditions such as oral thrush or vaginal yeast infections.
What Causes Candida Overgrowth?
Candida overgrowth is most common in immunocompromised patients, those with uncontrolled diabetes, or those who have recently or frequently used antibiotics since antibiotics can kill off both good and harmful bacteria, unbalancing yeast levels.
Additionally, certain medications, high levels of stress, and increased alcohol intake may lead to candida overgrowth.
How Does the Candida Diet Work?
The candida diet aims to limit yeast and sugars to reduce the amount of candida in the gut and restore balance to the bacteria and yeast that live in your body. In addition, the candida diet focuses on foods that reduce inflammation and regulate blood sugar.
A complete candida cleanse often lasts four to six weeks and prioritizes eating lean proteins, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables. Followers should avoid:
- Processed, refined-flour, and refined-sugar foods
- Gluten
- Sweeteners
- Dairy
- Sugary foods, like ice cream and candy
- Mushrooms
- Alcohol, especially beer, wine, and hard ciders
While following a diet to increase fiber, eliminate junk food, and drink more water is almost universally beneficial to your health, you should always check with your primary physician before starting a diet, especially one that restricts carbohydrates.
Most patients who follow a candida diet for the recommended four to six weeks report a lift in brain fog, bloating, indigestion, fatigue, nausea, and gas.
Suppose that you’re concerned about restoring balance to your gut microbiome and reducing or eliminating digestive concerns, aches and pains, and other issues that may stem from candida overgrowth. In that case, a candida diet may be worth considering.

by Stemedix | Aug 1, 2022 | Chronic Pain, PRP
Pain serves an essential purpose in the body. It triggers an unconscious physical response, warning you that something is causing harm and that you need to react. For example, if a hot stove burns your hand, pain tells you to jerk your hand away before it sustains more damage. In this article we talk about treating chronic pain.
However, chronic pain works differently. Chronic pain may stem from an illness or an old injury you should have overcome, but the pain persists. Some patients experience chronic pain from an ongoing condition, such as arthritis. Acute pain becomes chronic if it lingers for twelve weeks or more despite treatment and medications.
Chronic pain is challenging because there isn’t always a clear cause. Most chronic pain patients try to manage their suffering with medications, therapies, and targeted exercises. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy offers a natural alternative option for potential benefits.
Platelet-Rich Plasma Treatments
Blood consists of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma binds the three cell types together. When you’re wounded, platelets rush to the injury site to clot the blood and stop the bleeding. Platelets also contain proteins called growth factors that promote healing in the wound.
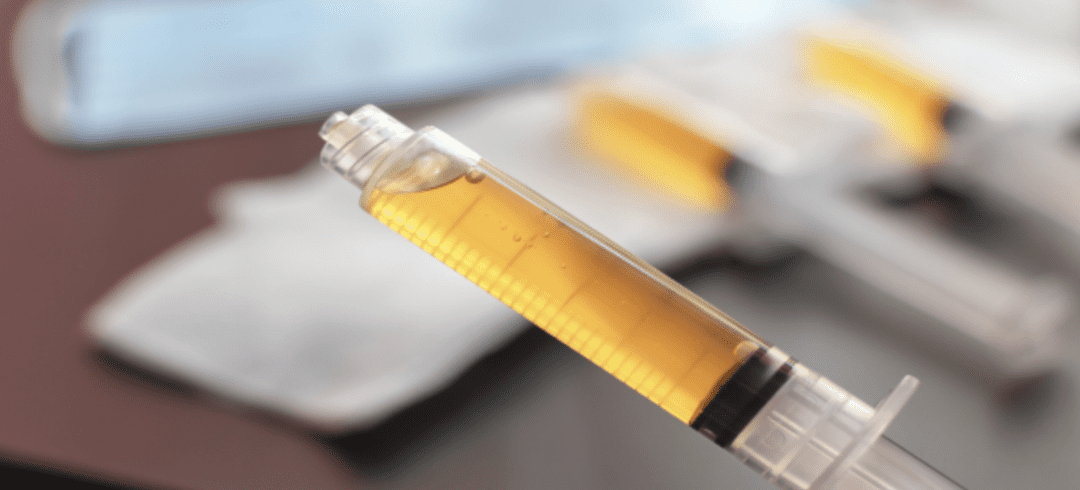
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments start by drawing blood from a patient. Then, the blood is placed in a centrifuge to separate the platelets and plasma from the red and white blood cells. The plasma is now called “platelet-rich” and is administered to the injury or pain site.
How Does PRP Treat Chronic Pain?
Once PRP enters the location that causes pain or inflammation, the growth factors in the solution stimulate the body’s natural healing response. As a result, the PRP begins repairing damaged tissue, restoring normal functions, and reducing inflammation and swelling.
As the inflammation in the site decreases, pain and swelling may begin to diminish, and the patient may start to see improvements in range of motion and strength.
How Does PRP Compare to Cortisone Injections?
Both PRP and cortisone injections can provide relief to patients suffering from chronic pain. However, cortisone or corticosteroid injections only provide a temporary solution. In addition, cortisone injections might cause deterioration in the ligaments, bones, and joints.
While cortisone injections provide immediate relief, PRP injections have the potential to stimulate tissue regeneration and healing, relieving pain gradually as the area heals. The treatments may require some time to take effect, but they can provide enduring benefits. While PRP is a new treatment option for those suffering from chronic pain, it offers promising, healing results well beyond masking pain symptoms. If you would like to learn more about how PRP injections can help with treating chronic pain, Contact Stemedix today!

by admin | Jul 29, 2022 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells, and specifically mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have long been considered as a promising therapeutic agent for the treatment of a wide variety of degenerative and ischemic diseases. Over this time, MSC immunomodulation, their capacity for multilineage differentiation, and their ability to self-renew have been well established and are now considered to be clinically relevant.
Considering this, scientists have hypothesized that the therapeutic application of MSCs in immune/inflammatory contexts may be more efficacious than other, more traditional approaches currently used in the field of regenerative medicine.
In this review, Wang et al. specifically focus on the non-traditional use of MSCs as a potential treatment towards immune/inflammatory-mediated diseases and identify important findings and trends in this area of study as they relate to specific immune/inflammation-mediated diseases, including graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), multiple sclerosis (MS), joint diseases [including Osteoarthritis (OA) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA)], inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and inflammatory airway and pulmonary diseases.
While there have been several promising results indicated in a number of trials using MSC for treatment of GVHD, the same results have not consistently been observed in all trials. One potential reason for the observed difference in results could potentially be a result of heterogeneity observed in conducted trials. Significant observed differences included those between pediatric and adult patients, the type of stem cell transplanted, as well as the MSCs utilized. Interestingly, there has also been a significant difference between results of published trials occurring in Europe (generally positive) compared to those trials occurring in North America (more equivocal results). While MSCs have strong potential for use as a therapeutic agent for GVHD, additional study into patient population and stringent MSC processing criteria are required before consistent and reproducible results are able to be delivered.
As of the publication of this review (2016), Wang et al. identified 23 registered clinical trials using MSCs for the treatment of MS. Additionally, animal models exploring the use of MSCs for the treatment of MS have demonstrated strong therapeutic effects. While many of the clinical trials using MSCs for the treatment of MS were ongoing, several animal models and many additional preclinical studies demonstrated MSCs to have therapeutic efficacy for the treatment of patients with MS.
Since cartilage cannot regenerate, the use of MSCs in treatment of joint diseases are considered a strong therapeutic option for several of these conditions, including OA and RA. Considering that prevention of inflammation and immune attacks on joints must occur in order for the joint repair to occur, and considering the immunosuppressive properties associated with MSCs, MSCs are thought to be well suited for use in the treatment of OA – a thought that has been well supported in both small and large animal studies.
Additionally, several of the 38 clinical trials underway at publication of this review indicated positive results in reduction of OA-induced pain and other related symptoms and for joint repair as observed by cartilage regeneration. On the other hand, similar results have not been observed for RA. The authors point to the detailed mechanistic differences between RA and OA as the likely reason for the observed therapeutic differences observed between the two joint diseases.
The 19 clinical trials and several animal model studies have overwhelmingly demonstrated that MSC therapy is both safe and a highly viable therapeutic option for the treatment of IBD, especially CD fistula formations.
Considering that between 80-90% of MSCs delivered intravenously have been observed to rapidly reach the lungs, MSC therapy has been thought to be particularly well suited for treatment in several pulmonary diseases, including COPD, asthma,emphysema, and even pneumonia. However, while animal models and preclinical studies have demonstrated MSCs to be safe in this application, the 29 registered clinical studies using MSCs for pulmonary disorders have also indicated the application to be safe – but have yet to replicate the efficacy observed and reported in the previously mentioned preclinical animal studies.
The authors of the review conclude that hundreds of clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of MSC therapy in this application have demonstrated their use to be safe. However, the overwhelmingly positive results reported in preclinical animal studies have not yet been observed through these clinical trials. Considering these findings, Wang et al. call for a better understanding on both the mechanistic properties of MSC Immunomodulation and the pathophysiological details and subsets with specific disease entities as a way to better tailor MSC therapy.
Source: “Human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) for treatment towards ….” 4 Nov. 2016, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5095977/.

by admin | Jul 27, 2022 | Multiple Sclerosis, Health Awareness
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks the brain, spinal cord, and the rest of the central nervous system. The National Multiple Sclerosis Society states there are, on average, one million people in the United States living with this disease.
One treatment that has the potential of offering an improvement in the symptoms of MS is biotin. Learn what biotin is and what it can offer.
What Is Biotin?
Biotin is also known as vitamin B7. It is one of the B-complex vitamins essential for nerve cell metabolism and is present in many foods, including:
- Egg yolks
- Chard
- Brewer’s yeast
- Nuts
- Livers
- Soybeans and other legumes
- Whole grains
- Bananas
- Mushrooms
- Cauliflowers
Biotin is a part of enzymes that break down fats, carbohydrates, amino acids, and other substances. It also has links to healthy nails, hair, and skin.
How Biotin Can Help Combat MS
Biotin can work to combat MS by stimulating enzymes that help produce more myelin. Myelin is a layer that wraps around your nerves and increases the rate at which electrical impulses travel, and when the immune system targets and damages myelin, multiple sclerosis develops.
Having healthy levels of myelin makes it possible for nerve cells to communicate better, which can relieve symptoms of MS and might even slow the disease’s progression. As such, a supplement such as biotin that encourages myelin production can be very helpful in managing MS.
In some studies, people with MS saw an improvement in their vision upon taking biotin. Another study showed that those taking high doses of biotin felt a reduction in pain levels as well as a boost in energy and a reduction in paralysis.
Learn More About Biotin
Biotin has the potential to offer relief from symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Whether it is the right choice for you will depend on many factors, including your doctor’s recommendations.
If you have MS and are interested in exploring biotin, contact us to learn how you can order today.

by Stemedix | Jul 25, 2022 | Stem Cell Therapy
Fibromyalgia is often misunderstood and misdiagnosed. It’s estimated that up to 2% of adults in the United States suffer from the condition, with women affected almost twice as frequently as men. Here we will learn about Stem Cell Therapy for Fibromyalgia.
What Is Fibromyalgia?
Fibromyalgia is a medical condition where sufferers experience widespread pain throughout their bodies. In addition, they can also endure sleep disturbances, fatigue, and emotional and mental distress.
Patients with fibromyalgia may also be more sensitive to pain, a condition called abnormal pain perception processing. While the origin of fibromyalgia is unknown, experts believe a malfunctioning nervous system may be the cause.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine aimed at managing the root cause of pain and disease. Stem cells lie dormant throughout the body until they’re activated as part of a healing response.
Mesenchymal stem cells are different from other cells found in the body, as stem cells are the only cells that can differentiate into specialized cells instead of solely producing more stem cells.
When stem cells divide, they can create another stem cell and a specialized cell, like a blood cell or a muscle cell. The specialized cell can then heal or replace damaged cells.
How Can Stem Cell Therapy Treat Fibromyalgia?
Current treatments for patients with fibromyalgia include prescription and over-the-counter medications, stress management techniques, cognitive behavioral therapy, and exercise. While these treatments are often effective, they don’t address the underlying cause of fibromyalgia.
However, many studies examining stem cells for managing fibromyalgia offer promising results. In addition, stem cell therapy’s potential in managing autoimmune disorders may also provide the key to fibromyalgia treatments.
Stem cells possess immunoregulatory properties that help to manage the body’s immune response and reduce inflammation. Patients with conditions aggravated by inflammation, especially those in the nervous system, may find relief as the inflammation subsides.
Specifically, stem cell therapy treatments targeting neuroinflammation in the brain may offer the potential to correct signals in the nervous system and reduce abnormal pain perception processing.
Additionally, stem cells release growth factors or cytokines into their injection points. The growth factors serve as part of the process of replacing damaged cells. Researchers believe that patients with fibromyalgia may have a unique cytokine profile that increases inflammation.
Explorations in stem cell therapies for fibromyalgia show that the new cytokines may repair and replace the pro-inflammatory cytokines aggravating the condition.
Fibromyalgia Patients May Soon Find Relief
As studies and trials exploring the benefits of stem cell therapy in managing fibromyalgia continue, patients may soon have a new treatment option that targets the cause of the condition instead of simply managing symptoms. Patients are already beginning to see results in several preliminary treatments. If you would like to learn more about Stem Cell Therapy for Fibromyalgia, contact us today at Stemedix!


 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
