
by Stemedix | Jan 24, 2022 | Stem Cell Therapy, Pain Management
Patients who suffer from ongoing intractable pain know how debilitating it can be. Pain becomes your default state as you try to cope with your chronic condition. Many chronic pain management methods only mask the underlying symptoms causing your pain. But there might be an option that helps chronic pain and potentially the underlying causes of the pain. Here we talk about stem cell therapy for pain.
Healing and Regeneration with Stem Cells
Stem cells do not have a specified function in your body until they are “programmed” into a certain role. Stem cell therapy can direct your new stem cells to the source of your chronic pain to potentially help the root of the problem. These cells help your body heal and regenerate important tissues that would otherwise remain damaged.
This type of therapy can reduce inflammation and pain at the site of injuries and damaged tissues. Stem cells speed up healing and bring extra resources to the parts of your body that need them most.
Chronic Pain Conditions
You might be wondering if you are a candidate for stem cell therapy. Depending on the underlying medical condition you suffer from, you could potentially benefit from stem cell treatments.
Some conditions that cause chronic pain include:
These are just a few of the chronic conditions that cause severe pain that may have potential benefits with stem cell therapy. This type of treatment may provide life-changing relief for many patients. When pain is part of your daily life, relief can bring you a whole new perspective on life.
Reduce Inflammation and Autoimmune Responses
A large number of chronic pain conditions fall under the autoimmune umbrella. These conditions are characterized by a lot of inflammation in your body. Inflammation is a healthy immune response when properly regulated by your body. However, excess inflammation can damage your tissue and cause chronic pain over time.
Stem cells travel to the sites of inflammation to produce anti-inflammatory responses. This helps your immune system regulate excessive responses to perceived threats. The result is that your pain may be greatly reduced, and your body can restore balance with inflammatory responses.
Cutting-Edge Chronic Pain Treatment
Stem cell therapy is a cutting-edge pain treatment that is backed by studies and research. Patients have shown great improvement after stem cell therapy in numerous studies. While stem cell therapy is not a cure for chronic pain conditions, it may improve your body’s pain levels. Patients are exploring this new alternative therapy to find options in their healing journeys. If you would like to learn more or schedule a consultation, contact us today!

by Stemedix | Jan 17, 2022 | Pain Management
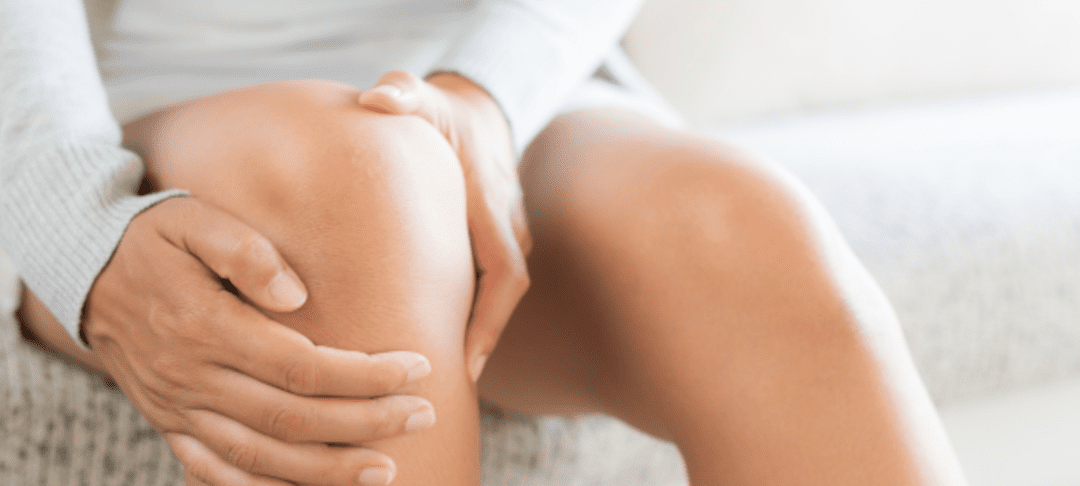
Knee pain can be debilitating and impair your ability to have a quality daily life. There are many causes of knee pain, and you might feel frustrated trying to navigate different knee pain management options. Some people experience chronic knee pain from sports injuries, arthritis, or old age. No matter what the cause of your knee pain is, there are options for relief. Here are some options when it comes to pain management for knee pain.
Medications
Your doctor might prescribe medication to treat your knee pain. There are various types of medications that help relieve knee pain issues. Anti-inflammatory medications can help with symptoms of osteoarthritis, an inflammatory joint condition that causes chronic knee pain. If you suffer from a condition like gout, your doctor may prescribe a specific type of medication to treat this underlying condition.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around your knee to provide more support and relieve pain. Exercises like knee stretches and mobility practice can help restore your knee function. Physical therapy for knee pain is often recommended after knee replacement surgery to prevent your knees from getting stiff and losing mobility.
Injections
Your doctor may recommend injections to treat your knee pain. Corticosteroids are a common type of injection for pain relief. They are most effective for treating arthritis-related knee pain. During an arthritis flare-up, the corticosteroids can put your body’s healing mechanisms into overdrive to reduce your pain.
Other types of injections, like platelet-rich plasma and hyaluronic acid, are available as well to help manage pain. These injections have shown some potential to treat knee pain, but they are still considered experimental.
Stem Cell Therapy
Another option being explored more these days for knee pain is regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy. This alternative option therapy has the ability to regrow important tissues and cartilage within the body. It has shown promising results in treating osteoarthritis, a common cause of knee pain.
Knee pain often stems from injuries or wear and tear on your knee joints and the surrounding tissues. Stem cell therapy can potentially replace some of the damaged tissues around your knee to relieve your knee pain. Since stem cells start as a blank slate, they can be grown into almost any type of cell that your body needs.
Stem cell therapy has shown few negative side effects for patients who have received treatment. If you suffer from knee pain and do not see results from other forms of treatment, stem cell therapy might be a good option to explore to help manage your knee pain for relief. If you would like to learn more, contact us today and speak with a care coordinator.

by admin | Oct 20, 2021 | Health Awareness, Pain Management
Millions of people rely on oral supplements to mitigate the effects of joint pain and arthritis. While these supplements can provide some relief, it is important to choose the right products. A few of the more popular options include glucosamine, omega-3 fatty acids, and chondroitin.
If you or a loved one are struggling with joint pain, then you may want to consider adding these supplements to your daily regimen:
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays an important role in bone strength. Inadequate levels of vitamin D can contribute to injuries and joint pain. Oral vitamin D supplements are affordable and can help you avoid these potential issues.
Glucosamine
Your body uses glucosamine to maintain healthy cartilage. Since cartilage acts as the cushion or shock absorber for your joints, it is essential for preventing joint pain. Glucosamine also has anti-inflammatory properties.
Chondroitin
Many glucosamine supplements also contain chondroitin. Together, these two supplements can reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis. Chondroitin has been linked to better mobility, reduced pain, and less dependence on pain medications.
Omega-3
Omega-3 supplements like fish oil are often discussed due to their potential heart health benefits. However, they may also help reduce stiffness associated with chronic inflammation.
Curcumin/Turmeric
Curcumin, which is the active ingredient found in turmeric, has been linked to joint pain relief. This treatment likely works because curcumin has strong anti-inflammatory properties.
Green Tea
Green tea is packed full of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory micronutrients. As a result, it may be beneficial for combating joint pain and stiffness. However, more research is needed to understand its effects fully.
While all of the supplements outlined above can help reduce arthritis and joint pain severity, medical intervention may still be necessary. In the past, this meant potentially harmful oral medications or invasive surgical procedures.
Another possible treatment option is stem cell therapy. While stem cell therapy is still being studied, many patients have experienced benefits using this intervention. It has allowed them to regain a better quality of life while also avoiding invasive surgery or healing from surgery.

by Stemedix | Sep 27, 2021 | Pain Management, Stem Cell Therapy
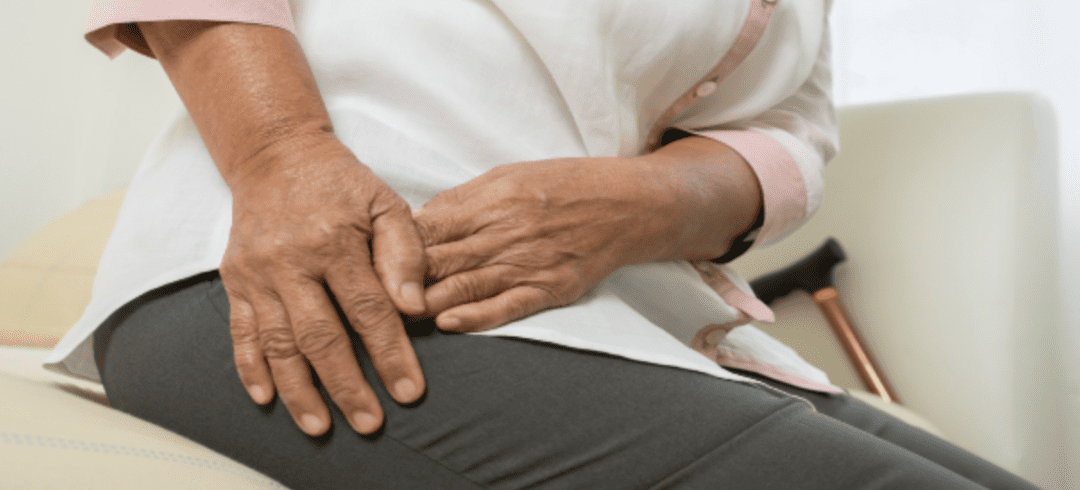
Joint arthritis is a very common condition that causes pain. According to some research, nearly half of adults over 65 suffer from arthritis of the joints. Aging causes wear and tear to the cartilage that protects the joints. While there is no way to fully prevent this wear and tear, innovative technologies are available to manage joint arthritis pain.
Some patients have found potential alternative options to help manage pain and inflammation with regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy. Below, we will discuss the potential benefits of stem cell treatments for joint arthritis pain.
Why Does Joint Arthritis Happen?
When the cartilage in a joint begins to break down, the associated bones may rub together. This can be incredibly painful. It can also lead to swelling, stiffness, and decreased range of motion for a patient.
There are several different types of joint arthritis. One of the most common types is osteoarthritis. This is also known as “degenerative” arthritis. Degenerative arthritis is often the result of using a particular joint for many years. It usually appears when patients are middle-aged and progresses as they get older. But younger people are susceptible to this condition, as well.
Joint pain can also result from a condition called Rheumatoid Arthritis. This is an autoimmune disease that can lead to inflammation and pain. Infection and gout can also account for ongoing joint pain.
Common Symptoms
Usually, arthritis will cause aching or throbbing around a single location. The following joints are some of the more common areas affected: hips, shoulders, wrists, knees, hands, and feet.
In some cases of joint arthritis, the pain can be spread throughout the body along with pain concentrated around damaged joints.
No matter what the underlying cause of their joint pain is, many patients are exploring stem cell therapy to help manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Stem Cell Therapies for Joint Pain
Stem cells are a type of simple human cell. As such, they are present in the human body naturally. These simple cells act as an instructional system for repairing and healing certain bodily tissues. Stem cell treatments involve isolating and reintroducing these reparative cells into damaged areas of the body.
Our natural stem cells may not be enough to help with joint arthritis and for this reason, stem cell therapy provides a concentrated amount of mesenchymal stem cells to be administered systemically and to problematic areas.
Many patients have reported pain and inflammation relief as well as tissue repair outcomes through these innovative and minimally invasive stem cell therapies. If you would like to learn more contact us today!

by Stemedix | Sep 13, 2021 | Stem Cell Therapy, Pain Management
Hips are some of the strongest and largest joints in the body. They support the body’s weight and provide a wide range of motion. Despite their power, hips are susceptible to disease, trauma, and gradual degradation. Over time, hip joints can succumb to many different pathologies. For example, osteoarthritis is one of the leading causes of pain in the hip. This can result from chronic overuse. Hip pain can result in many serious consequences. For instance, hip pain can limit a patient’s mobility and affect their ability to sleep. Pinched nerves, certain types of cancers, and infections can all lead to hip discomfort. Here we answer the question, How long does stem cell therapy last for hips?
Treatments for Hip Pain
There are many traditional medical treatments for hip joint discomfort. They include:
- Pain medication
- Rest
- Arthroscopic surgeries
- Physical Therapy
- And more
In severe cases, hip replacement surgery may be necessary. Hip surgeries can be very difficult for patients. In many cases, they may result in significant pain and long recovery periods. Thankfully, there are options beyond traditional treatments for hip pain.
Research over the past several decades has indicated that regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy, may be useful for treating hip pain.
Understanding Stem Cell Treatments
Stem cells are one type of simple cell that the human body produces. They can stimulate the growth of new tissue in many areas and systems in the body. Beyond that, stem cells encourage the body’s natural healing processes. These simple cells can be used to differentiate and potentially regenerate tissues.
In some cases, healing can be difficult when not enough stem cells are produced in a certain area. This sometimes contributes to hip pain and discomfort. The introduction of stem cells into a problem area can help motivate the growth and renewal of tissue in the hip joint. Stem cell therapies also have the potential to reduce painful inflammation in the hips and other joints.
Stem cell treatments are minimally invasive and have been shown to be safe. Some patients have used stem cell therapies to prevent the need for painful surgeries.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Hips
Stem cell therapy for hips, also known as regenerative medicine for hip joints or hip joint stem cell treatment, involves the use of mesenchymal stem cells to repair and regenerate damaged hip joint tissue. This type of therapy is especially beneficial for those with hip osteoarthritis, a condition where the cartilage in the hip joint wears down, causing pain and stiffness. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for hip osteoarthritis has been shown to improve pain, increase joint function, and promote tissue repair and regeneration. Stem cell hip regeneration and hip joint tissue repair using stem cells are promising treatments that offer an alternative to surgical interventions and can significantly improve the quality of life for those suffering from hip joint problems.
How Long Do Stem Cell Treatments Last?
So, how long does Stem Cell Therapy last for hips? In most cases, patients treated with stem cell therapies can return to their normal activities within six weeks.
The length of improvement in the patient’s hip pain may vary, depending on their condition. However, many patients have experienced years of hip pain relief from stem cell therapies.
Also, the minimally-invasive nature of stem cell therapies allows patients to receive further treatments, if necessary. This innovative approach to hip pain relief provides an exciting opportunity for patients everywhere. If you are interested in booking a consultation with a care coordinator contact us today at Stemedix!

by Stemedix | Apr 5, 2021 | Chronic Pain, Pain Management
Spinal stenosis flare up occurs when the spaces in the spine become narrow, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. Changes related to aging are a common cause for the condition, but it can also be a result of congenital factors; some people are simply born with a narrower spine. Other spinal conditions such as scoliosis can also be a risk factor for the condition.
There are two regions where spinal stenosis can occur: the lower back or the neck. Common symptoms include pain in the affected area, as well as numbness or weakness in the arms and legs. Treatment for the condition may vary based on the severity of symptoms. For mild cases, doctors may simply recommend routine monitoring and home remedies such as pain relievers, heat and cold therapy, and exercise. In more severe cases, treatments such as a decompression procedure may be recommended to remove portions of ligaments that are compressing nerve roots. Spinal stenosis surgery is usually reserved for only the most severe cases, including those with pronounced pain or loss of bladder control.
How Long Does a Spinal Stenosis Flare up Last
The recovery period for lumbar stenosis varies depending on the individual patient and the treatment approach implemented. While each case is unique, it is generally observed that most patients experience significant recovery from spinal stenosis within a timeframe ranging from six months to one year after initiating treatment. It is important to note that specific circumstances, such as the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of the chosen treatment methods, can influence the recovery duration.
Avoiding Spinal Stenosis Flares
Because spinal stenosis is largely due to age-related factors, including bone and muscle loss, there’s no way to completely guarantee full prevention of spinal stenosis. With that being said, certain factors could contribute to the condition or cause flare-ups in existing cases. Here are some factors to watch for:
- Being overweight: Carrying extra weight puts excess strain on the spine. Maintaining a healthy weight through a nutritional diet and exercise are good ways to control symptoms or minimize your risk for the condition.
- Smoking: Researchers have established a link between smoking and back conditions that require spinal surgery. In particular, smoking appears to increase the risk of a narrowed lower spinal space. Smoking cessation can help reduce the risk.
- Poor Posture: Your posture plays an important role in maintaining spinal health. Poor posture can shift the alignment of the tissues in the back, aggravating preexisting conditions such as spinal stenosis. Using ergonomic furniture and taking breaks to sit or stand frequently throughout the day helps promote good posture.
- Inactivity: Exercise keeps the muscles that support the spine strong, and can also help you maintain flexibility and balance. Periods of inactivity can have the opposite effect and may contribute to flare-ups.
Tracking your symptoms is important with spinal stenosis flare up, as the condition can develop slowly over time. Lifestyle treatments and avoidance of known triggers may help to control your pain for a long time, but if you tried these methods and are still experiencing discomfort, it may be time to consider other treatment options.
Some patients are discovering the healing potential of stem cell therapy options. The cells have the potential to help with inflammation, pain, and regeneration of tissues. It is important to have a regenerative medicine spine specialist review candidacy to determine if the outcome is optimal for the patient. Discover if you are a candidate with a complimentary assessment.
Schedule Your Appointment
If you’re seeking an advanced and effective treatment for spinal stenosis, look no further than Stemedix. We are a trusted provider of stem cell therapy, offering a cutting-edge solution for individuals living with spinal stenosis.
Our stem cell treatment for spinal stenosis involves the utilization of mesenchymal stem cells, which have the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types and stimulate tissue repair. These stem cells are derived from your own body’s adipose (fat) tissue or bone marrow, ensuring compatibility and minimizing the risk of rejection or adverse reactions. Contact us today!




 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
