
by admin | Feb 9, 2022 | Health Awareness
Inflammation is part of the body’s natural response to injury and infection. However, sometimes the body’s inflammatory response works overtime, causing several health conditions.
Good Inflammation
When the body is working correctly, inflammation occurs when you’re sick or injured. This kind of inflammation is a good thing. Chemicals in the bodywork to fight infections and heal injuries by heading to damaged tissues to treat them with blood, fluid, and proteins or by protecting and repairing damaged tissues with swelling and heat.
This good, or “acute,” inflammation gathers up immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators to clear out damaged tissue, initiate repairs, and eliminate the cause of cell injury. One of the key elements of acute inflammation is that it goes away once it does its job.
Bad Inflammation
In contrast, bad inflammation occurs when your body has an inflammation response without injury or illness. The body’s immune response can overfire, which causes low levels of inflammation that can’t seem to dissipate, causing bad, or “chronic,” inflammation.
Chronic inflammation can cause problems of its own and is a factor in conditions like arthritis, asthma, atherosclerosis, blindness, cancer, and diabetes.
What Causes Bad or Chronic Inflammation?
Common causes of chronic inflammation include:
- An undiagnosed food sensitivity
- Exposure to irritants, such as environmental pollutants
- Chronic stress
- Autoimmune disorders
Identifying the causes of chronic inflammation serves as an essential step in treatment.
Determining the Cause of Chronic Inflammation
There are many ways your healthcare provider can work with you to identify the cause of your chronic inflammation. Some tests that may determine inflammation causes include:
- Food sensitivity testing
- Fatty acid profile
- Inflammation Patient Assessment Panel, which tests:
- High sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP)
- IL-6
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Ferritin
- Fibrinogen
- TNF-a
- Element analysis
In addition to testing for the source of your inflammation, you may also benefit from altering your diet to include anti-inflammatory foods, which may help your body calm its inflammatory response. For example, the foods included in the Mediterranean diet may provide some relief and support your immune response.
by Shoot To Thrill Media | Feb 8, 2022
Personalized Pain Management We combine traditional pain management with personalized regenerative medicine for a more individualized personal experience. Using advanced metabolic testing, microvascular and autonomic assessments, and health DNA, we create a personal...

by Stemedix | Feb 7, 2022 | Chelation Therapy
Primarily used for metal poisoning, chelation therapy is emerging as an alternative treatment for other conditions. Many places worldwide practice chelation therapy as alternative medicine, and it is now gaining in popularity in the US for treating a variety of conditions.
The History of Chelation Therapy
The word chelation comes from the Greek word chelos, meaning claw. The word claw refers to how metals in the body may bind to the chelating agent in a claw-like manner.
First used clinically in 1956 to treat patients with lead poisoning, chelation therapy is an established, effective treatment for patients suffering from metal poisonings.
How Does It Work?
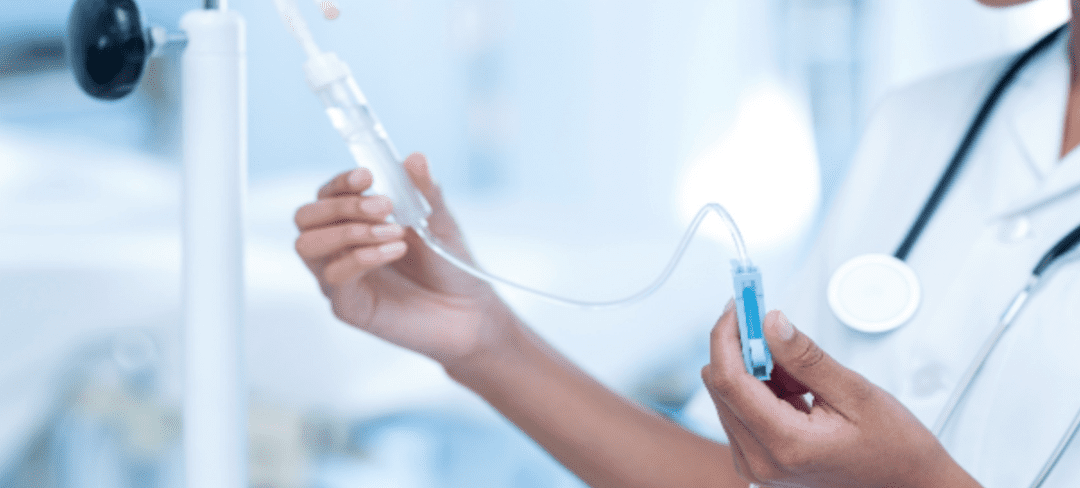
Physicians typically administer chelation therapy using weekly IV treatments, lasting approximately 30 minutes in length. First, a healthcare provider dispenses a chelator or chelating agent into the IV. The chelator then circulates through the bloodstream and binds to metals.
The chelator collects all of the metals in the bloodstream, forming a compound that the kidneys eliminate through urination. The most common chelator is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), which removes lead, iron, copper, and calcium. Other chelating agents include:
- Dimercaprol
- Succimer
- Deferoxamine
- Penicillamine
- Deferasirox
A healthcare provider chooses the proper chelating agent based on the patient’s health, age, and condition.
What Conditions Does Chelation Therapy Treat?
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) only approves chelation therapy to treat metal poisoning. However, some health providers are using this therapy to treat other conditions. Common conditions treated include heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease.
Chelation Treatment and Heart Disease
Atherosclerosis is the buildup of plaque in the arteries, leading to heart disease over time. Proponents of using this therapy to treat atherosclerosis believe that chelators can potentially bind to the calcium found in plaque, thus loosening blockages and preventing a buildup.
Chelation Treatment and Alzheimer’s Disease
Based on the belief that a buildup of aluminum in the brain causes Alzheimer’s disease, the chelator’s ability to bind and remove metals from the bloodstream may potentially provide relief from this degenerative disease.
Chelation Treatment and Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s patients are known to experience a buildup of iron in the brain. While it’s not entirely clear how the buildup of iron affects Parkinson’s patients, proponents of chelation treatment believe that removing the iron has the potential to benefit those suffering from Parkinson’s disease.
The Future of Chelation Treatment
While the FDA is still investigating the potential use of this therapy for various conditions, many healthcare providers are optimistic about its future. Patients looking to learn more about chelation therapy should reach out to their healthcare provider to know if it’s right for them. If you would like to learn more, contact a care coordinator today and schedule a free consultation.

by admin | Feb 2, 2022 | Health Awareness
Beans really might be a magical fruit. Recent studies find beans to be nutritional powerhouses rich in fiber, resistant starch, and plant protein. Adding beans to your diet promotes weight loss, insulin sensitivity, and cardiovascular health.
However, the power of a tiny bean may be even more impressive than previously thought. New studies on the body’s gut microbiome reveal that this internal ecosystem may affect our overall health in significant ways and that beans may be the key to unlocking its powers.
The Gut Microbiome
The human body’s microbiome is a collection of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and microorganisms that live throughout the body’s surfaces, like the skin and the digestive tract. However, most of the microbiome lives in the gut, which contains over 1,000 species of bacteria and trillions of organisms.
The gut microbiome produces vitamins, develops immune responses, and enhances the benefits of food. For instance, the gut microbiome converts dietary fiber and resistant starch into short-chain fatty acids that protect the intestines’ cells and regulate metabolism.
How Do Beans Help Gut Health?
The large intestine’s bacteria rely on prebiotics to survive. Prebiotics serves as food for gut bacteria. When your body isn’t getting enough prebiotics through your diet, the gut bacteria need to find new food, which ends up being the immune defense on the surface of the intestinal lining.
While all plants contain probiotics, beans, which are full of fiber and resistant starch, are especially rich in prebiotics. In addition, beans’ ability to nourish the gut microbiome and promote short-chain fatty acids production helps kick your immune system into gear.
Additionally, as studies dig deeper into the species of bacteria living in the gut microbiome, researchers have discovered that people with multiple sclerosis lack a bacteria that breaks down isoflavones. This nutrient is also highly prevalent in beans.
As new studies into the gut microbiome find connections between chronic conditions and the foods and nutrients that offer potential remedies, beans may be a powerful tool in improving your overall health.

by Stemedix | Jan 31, 2022 | Pain Management, Degenerative Disc Disease
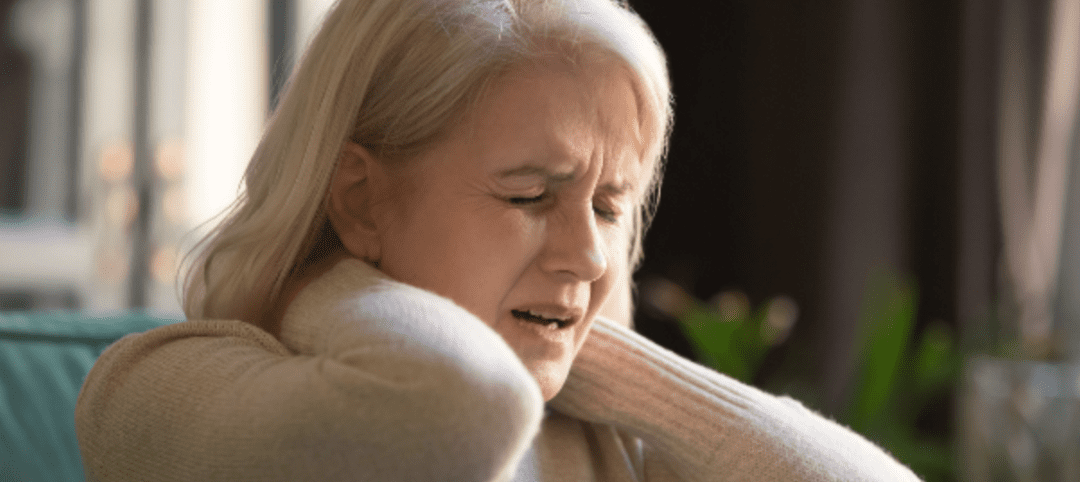
If you suffer from neck pain or pain that radiates down the arm, you may have cervical degenerative disc disease (CDDD). CDDD develops with the cushioning in the discs of the cervical spine (the neck) begin to break down. This breakdown can happen due to injury, genetics, or normal wear and tear. Without the natural cushioning for protection, discs may become herniated, or the patient may develop spinal stenosis or osteoarthritis. Here we will talk about Pain Management for Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease.
Can I Avoid Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease?
Nearly everyone develops CDDD as they age. However, there are lifestyle changes you can make to help improve the health of your spine and cervical discs. In addition to protecting spine health, the following tips may help decrease pain for those who are already experiencing the degenerative process:
Eat a Healthy Diet
Moderating your intake of salt, alcohol, and caffeine may help keep your spine healthy, as can eating a balanced diet full of fresh food and lean protein.
Stay Hydrated
Discs lose water as they age, so proper hydration plays an important role in maintaining disc health. Water also helps to deliver nutrients to the spine and carry away wastes.
Exercise
Daily walking, light stretching, strength training, and other low-impact exercise helps maintain flexibility in the cervical joints and reduce pain associated with cervical degenerative disease.
Quit Smoking
Nicotine inhibits bone growth and decreases the amount of oxygen that gets delivered to the discs as well as the rest of the body’s systems.
Practice Good Posture
Proper alignment when you walk and sit helps to reduce pressure on the spine. This practice not only decreases the amount of wear on spinal joints but also decreases pain. This is great for pain management for cervical degenerative disc disease.
Treatments for Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease
Surgical treatments can often be avoided if non-invasive treatments are applied. Traditional pain management techniques include:
- Prescription or OTC pain medications
- Hot/cold therapy
- Rest
- Physical therapy
- Massage, acupuncture, acupressure
Regenerative Medicine, also known as stem cell therapy, is a cutting-edge treatment offering potential to relieve pain from cervical degenerative disc disease.
Patients who have recently developed CDDD symptoms, as well as those who’ve been living with the painful condition for many years, may benefit from safe, non-invasive stem cell treatment. Studies have shown that patients receiving stem cell therapy reported:
- Fewer muscle spasms
- Improved strength and mobility
- A decrease in chronic pain levels
- Less tingling, weakness, and numbness in extremities
Regenerative medicine may also help improve other orthopedic conditions such as sport’s injuries, osteoarthritis, and musculoskeletal injuries.
Stem cell therapy is still considered experimental, and results are not guaranteed. However, it is a safe and minimally invasive treatment that could help CDDD patients manage their symptoms to help live a fuller, more active life free from chronic pain. If you are interested in learning more, contact us today and speak with a care coordinator.



 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
