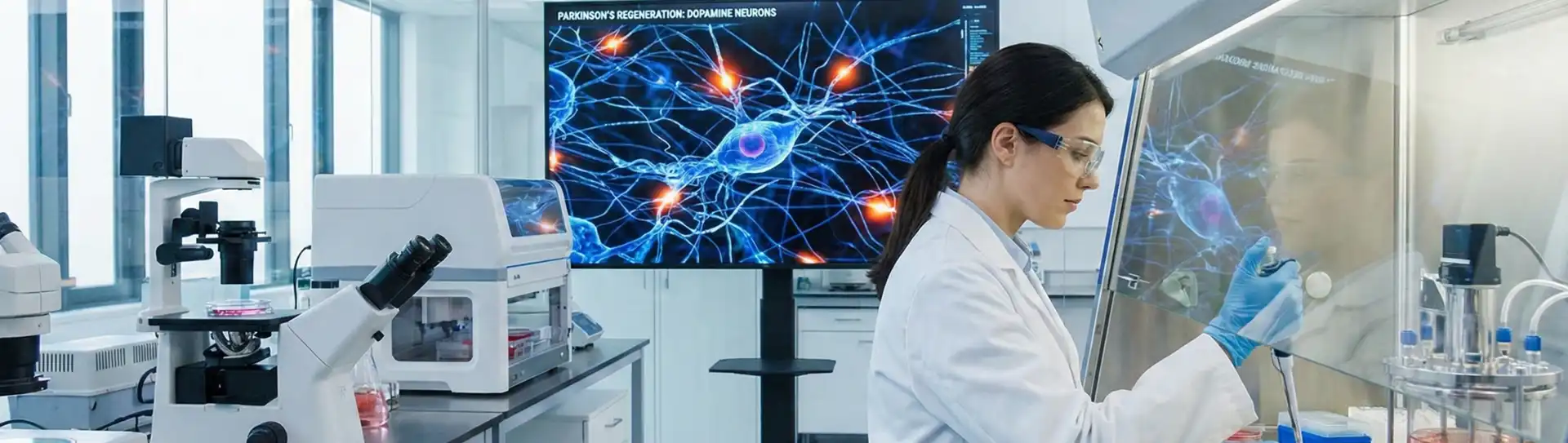
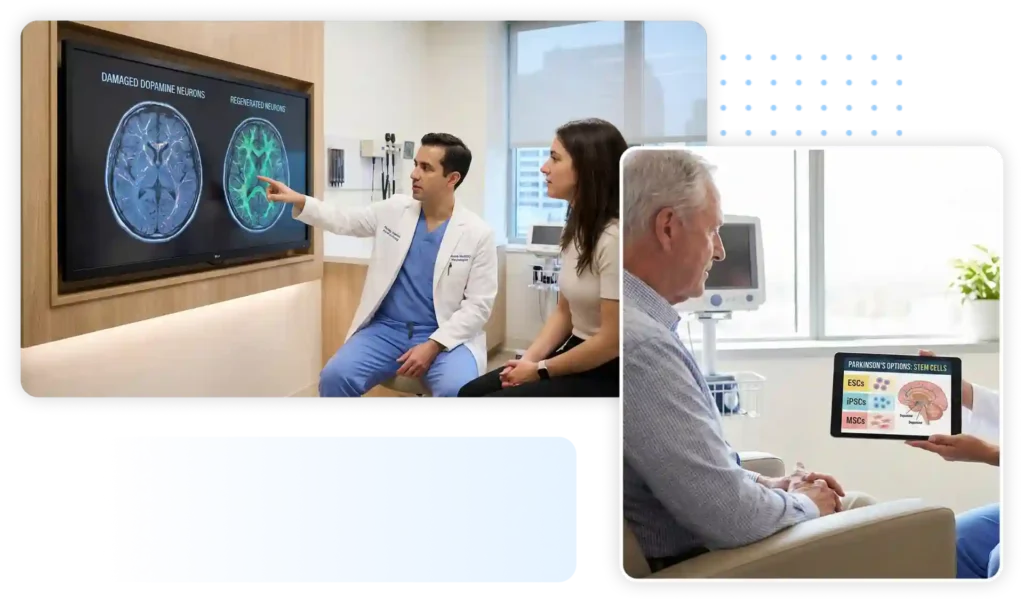
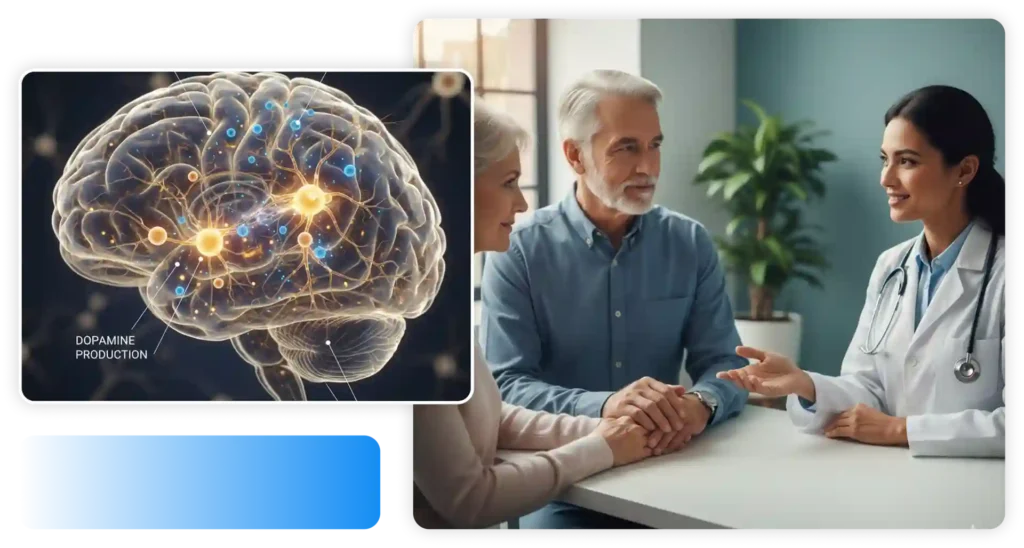
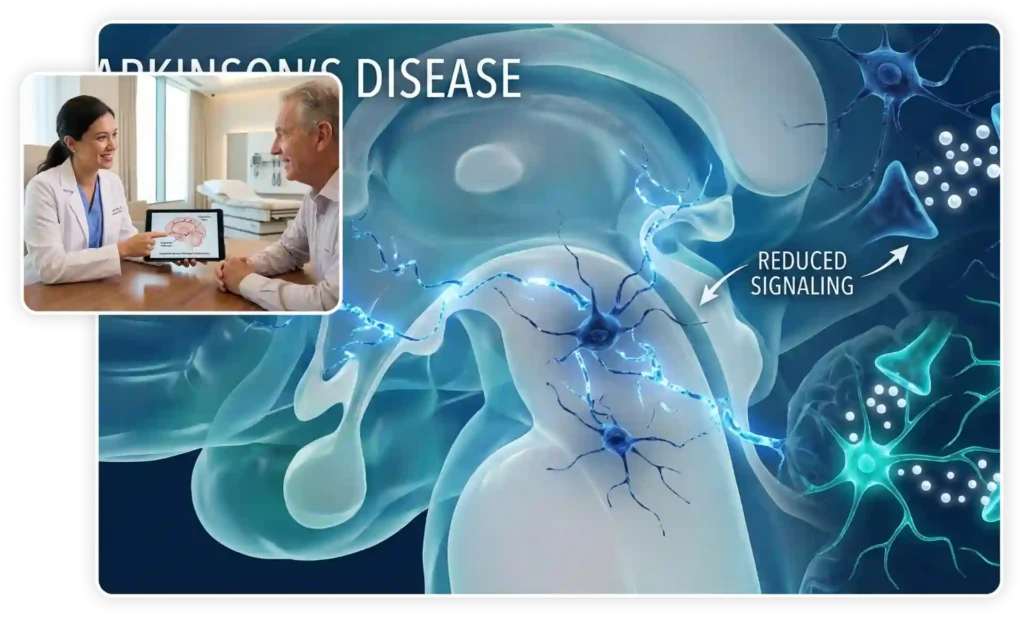
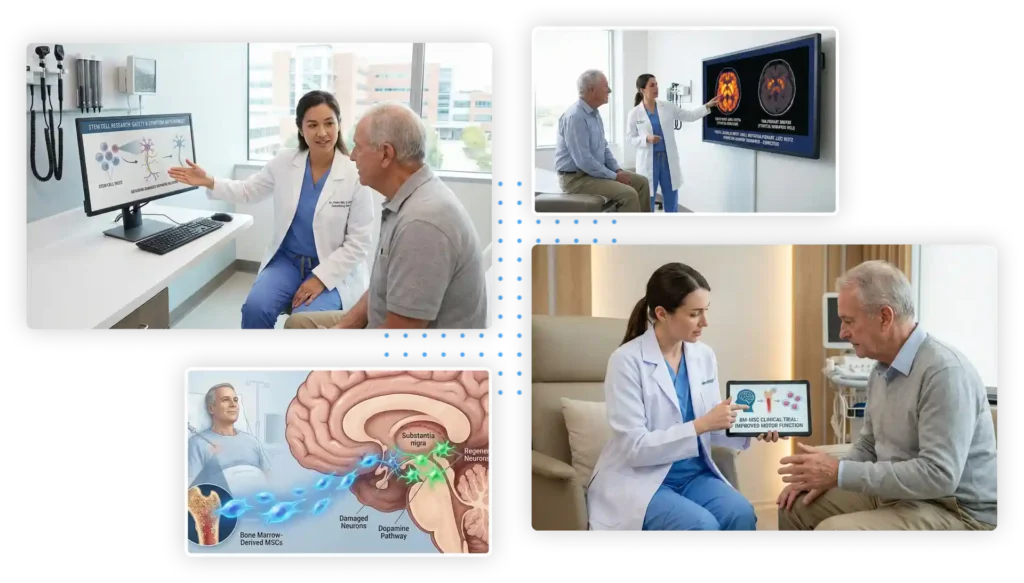
Regenerative Medicine for Parkinson’s disease targets the underlying cellular damage. Researchers have explored various sources of stem cells, including embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and adult stem cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). These cells possess the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types, including dopamine-producing neurons.
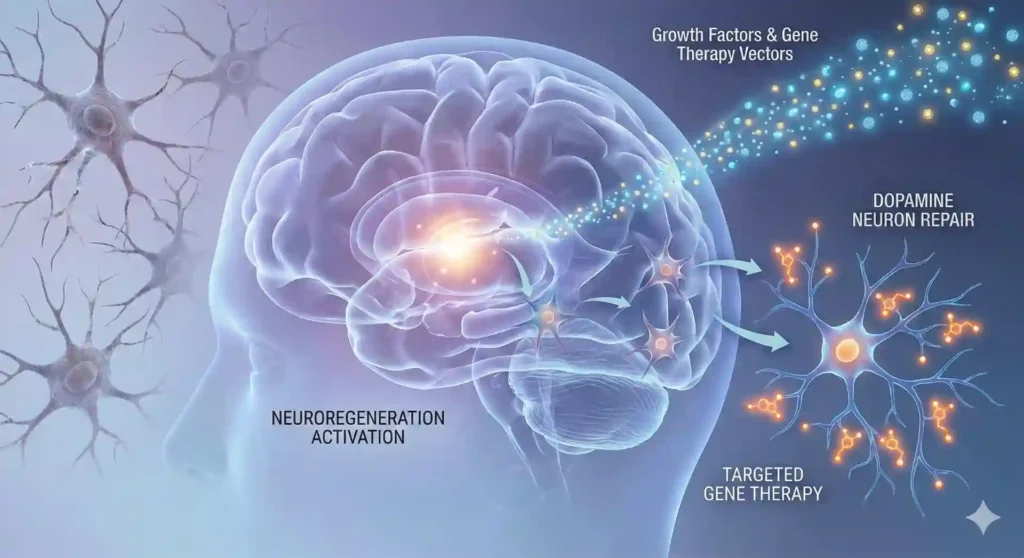
Transplantation of stem cell-derived dopamine neurons into the brains of Parkinson’s patients has shown promising results in preclinical and early clinical trials of stem cell treatment for Parkinson’s. These transplanted cells can potentially integrate into the existing neural circuitry, restore dopamine production, and improve motor symptoms. However, challenges such as immune rejection, ethical considerations, and refining the transplantation techniques still need to be addressed before widespread implementation.