
by admin | Aug 27, 2018 | Adipose, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Regenerative medicine is a field of research concerned with the process of replacing diseased, dying, or dead cells with the intent of restoring structure and function. In its most basic form, regenerative medicine seeks to regrow cells that were lost or damaged due to injury or condition. Examples of regenerative medicine applications include restoring heart cells after a heart attack, repairing brain cells in Alzheimer’s disease or after stroke, or regenerating T-cells in HIV/AIDS. The potential applications of regenerative medicine are virtually limitless.
Adipose-derived stem cells hold great promise in the field of regenerative medicine. The stem cells are multipotent, which means they can become any number of cell types. For example, adipose-derived stem cells can become osteocytes (bone cells), neural cells (nerve cells), vascular endothelial cells (cells that make up blood vessels), cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells), pancreatic β-cells (cells that produce insulin), and hepatocytes (liver cells).
Adipose- or fat-derived stem cells have one obvious advantage over bone marrow cells: they are much easier to obtain. Bone marrow stem cells require an uncomfortable/painful procedure to extract them from the center of the bone. Fat-derived stem cells, on the other hand, can be taken from fat pockets in any number of places just under the skin. This essentially combines a sort of liposuction with stem cell transplantation.
Adipose-derived stem cells are the subject of nearly 200 clinical trials worldwide. Even now, fat-derived stem cells are proving useful in several clinical conditions. Adipose-derived stem cells were shown to help people after they suffered from a heart attack, by reducing the size of the damaged heart and helping to restore heart function.
Another advantage of adipose-derived stem cells is that they present possess a tri-germ lineage differentiation potential, meaning they can differentiate into all three germ layers. In other words, they have the remarkable potential to become virtually any cell in the body. This means they can be applied to more than one disease state. In neurodegenerative diseases, such as post-stroke, adipose-derived stem cells could be used to create nerve cells (neurons) and the other main type of brain cell, called glia. Both cell types are destroyed during a stroke, and both are important for proper brain function.
As more results are published from dozens of clinical trials, we will get a clearer picture of the therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stem cells. Indeed, the future of regenerative medicine is very bright.

by admin | Aug 2, 2018 | Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy, Studies
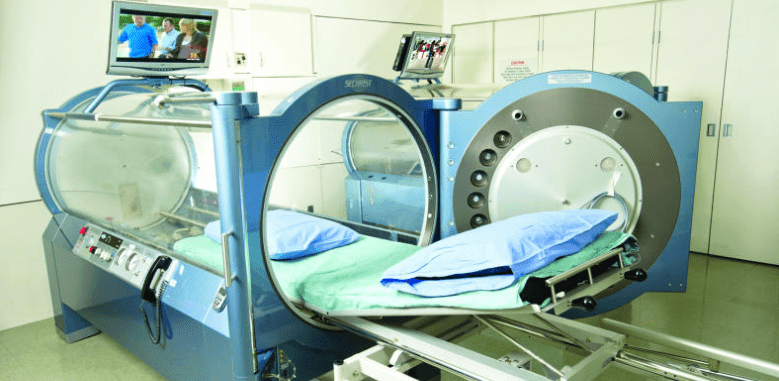
While most approaches to stem therapy involve infusing purified stem cells into the body, Thom and fellow researchers have shown that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is capable of stimulating the body to produce its own stem cells. Thom, Heyboer, and co-authors have extended this work by showing that by slightly increasing the pressures used during hyperbaric oxygen therapy, one can significantly increase the number of stem cells produced.
In his original work, Thom and colleagues showed that a single, two-hour session of 2.0 atmospheres (atm) pressure (twice the air pressure we normally feel at sea level) was capable of doubling the number of stem cells in the bloodstream. Twenty treatments increased stem cell levels by 800%. To study this phenomenon more closely, Thom’s research group recruited 20 patients to undergo hyperbaric oxygen treatment, some at the original 2.0 atm pressure, and some at 2.5 atm. The primary goal of this research was to find out whether a higher pressure was capable of eliciting a greater number of cells.
As before, treatment with 2.0 atm of hyperbaric oxygen substantially increased the number of stem cells found in the blood. However, treatment with 2.5 atm doubled or even tripled the number of stem cells produced compared to the 2.0 atm treatment session. In other words, a slightly higher pressure causes the body to produce substantially more of its own stem cells.
Researchers focused on two types of stem cells, in particular, CD34+ and CD45-dim—markers that appear on stem cells and/or progenitor cells. They are primarily found on cells in the bone marrow. Stem cells with CD45-dim generally go on to become bone, blood, or blood vessel cells, while CD34+ cells can differentiate into almost any cell. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is thought to stimulate the bone marrow to produce and release these stem cells into the bloodstream, which is the reason these treatments raise stem cell levels in the blood.
The results published by Thom and coworkers suggest that patients who wish to enhance the number of stem cells should consider undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Furthermore, the greatest number of stem cells was observed after 20 treatment sessions, suggesting that a greater effect occurs with more treatments.

by admin | Jul 27, 2018 | Health Awareness, Lupus, Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson's Disease, Studies
Colostrum is the milk produced by the mammary glands during pregnancy prior to giving birth. It is rich in antibodies that help prevent the newborn from various conditions. Colostrum as compared to normal milk contains a high amount of nutrients and fat, making it highly beneficial.
The most important thing to know about colostrum is that it is not a medication. It is a naturally designed food that maintains the health and prevents conditions. Colostrum is effective for shutting down the onset of conditions and infections, which helps the body to repair itself and allows the individual to enjoy a healthy and radiant life.
Colostrum is the Key to Gut Health
Colostrum is the source of everything that is required to maintain a healthy gastrointestinal tract. It is known that most of our conditions take birth in the gut and proper absorption of nutrients is the key to great health. It is one of the primary function of colostrum to maintain a healthy gut, which is the basis of the overall healthy body.
When the beneficial bacteria present in our intestine is outnumbered by the harmful bacteria then our gut is said to be out of balance. This imbalance has many consequences, one of which is the leaky gut syndrome.
Leaky gut syndrome is a condition due to which various pathogens and toxins pass through the lining of the gut and move freely in the body, this leads to various conditions. Leaky gut syndrome, if not treated can be a life-threatening condition.
Colostrum is an optimal treatment for treating leaky gut syndrome because it has growth factors that help repair the damage of the intestine to normal. It is also rich in immunoglobulins that control the pestering of fungi and bacteria in the body. In various conducted studies colostrum has successfully increased the surface area of the lining of the intestine, thereby improving the absorption of nutrients.
Colostrum: The Perfect & Functional Food
Looking at all the immune and growth factors that are present in colostrum, it is called the best alternative to pharmaceutical drugs, from steroids and antibiotics. Colostrum is also safe for people suffering from lactose intolerance and has no allergic reactions or side effects.
A functional food is one that has potential health benefits compared to normal food and is high in nutrients. Colostrum is high in nutrients and can be combined with other food products. It is most effective when taken on an empty stomach. Available in the form of capsules, colostrum is more effective and bioavailable.
Colostrum for Autoimmune Conditions:
Autoimmune conditions are those in which the body starts producing antibodies against itself. Colostrum has shown to be highly effective to treat autoimmune conditions like Lupus, Parkinson’s disease, and Multiple Sclerosis. Chemokine receptors have been observed to be the cause of the development of all these conditions. Colostrum produces antagonists of these receptors and has been shown to decrease the symptoms of many common autoimmune conditions.
Colostrum Used as a Topical Application:
Colostrum, if applied externally can help heal the burns, acne, cuts and various abrasions and even surgical cuts. If applied orally, it can help deal with sensitive teeth relieve canker sores and gingivitis.
Some Overall Benefits of Colostrum are:
Anti-inflammatory
Anti-aging
Anti-fungal
Anti-bacterial
Cancer
AuAutoimmuneondition
Blood pressure
Cholesterol
Sugar levels
Diabetes
Digestion
Flu prevention
Fat reduction
Heart health
Gut health
Immunity
Joint repair
Immunity
Mobility
Muscle repair
Pain
Stamina
Tissue repair
Wound healing
Weight loss
Inflammation
Below is a list of some common conditions for which colostrum can be effective:
Allergies
Anemia
Arthritis
Autoimmune conditions
Asthma
Bacterial infection
Bone marrow transplant
Cancer
Alcoholism
Allergies
Anemia
Arthritis
Crohn’s disease
Chronic fatigue
Diarrhea
Fibromyalgia
Food poisoning
Heart disease
Hepatitis
Influenza
Intestinal bowel syndrome
Joint repair
Leaky gut
Lupus
Multiple sclerosis
Osteoporosis
Obesity
Premature birth
Osteoporosis
Ulcer
Yeast infection
Viral infection
Where Can I Find Colostrum?
If you have any symptoms suggestive of gastro-intestinal dysbiosis (diarrhea, constipation, bloating, reflux, stomach discomfort or pain) then you should seek further work-up by your physician or a Functional Medicine Doctor.
In the meantime, it is recommended to start using Bovine Colostrum which can be found at Sovereign Laboratories at www.mysovlabs.com. Simply mix 2 tablespoons in 6oz of water and consume twice per day on an empty stomach. This product is full of gut healing immunoglobulins. Use for 2-3 months should result in significant improvement.
In addition, it is also recommended to take a good probiotic while using your bovine colostrum. Vitamin D levels should be optimized to levels between 80-100.

by admin | Jul 25, 2018 | Bone Marrow, Health Awareness, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells derived from bone marrow, or hematopoietic stem cells, are a topic of significant debate in the medical community. While they have exhibited significant potential for benefiting people with both cancerous and noncancerous diseases including immune deficiencies, not all methods for administering bone marrow are created equal. While intra-articular injections of bone marrow are more common and considered safer, intravenous methods pose serious risks, which are explored here.
Intra-articular injections involve injecting bone marrow directly into the compromised joint, whereas intravenous methods entail infusing bone marrow stem cells into the body through the veins. Intra-articular injections have shown promise in treating conditions such as osteoarthritis (OA) in joints such as the knee and has proven to achieve pain relief for moderate-to-severe cases of osteoarthritis.
Intra-articular treatments are localized, so the injected bone marrow is already in its target location upon being administered. According to research, this form of therapy is generally considered to be safe. In intravenous bone marrow transplants, however, there are serious risks associated with treatment. Bacterial infections are common, while viral and fungal infections can also occur and cause life-threatening conditions, such as organ failure.
Risk factors for developing any complication associated with intravenous bone marrow transplantations vary based on a number of factors, including the patient’s age, genetics, and type of disease being treated. With that said, due to its limited risks, intra-articular bone marrow methods appear to be the safest form of treatment currently available. Although each patient will need to discuss risk factors alongside potential benefits with his or her physician, oftentimes the risks appear to outweigh the potential benefits.
There are alternative therapies with fewer potential side effects which may be explored such as Adipose and Umbilical Cord-derived stem cells. These regenerative medicine treatments not only can treat osteoarthritis and sports-related injury conditions, but have also shown positive results in treating neurological conditions such as Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Post-Stroke, and Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI).

by admin | Jul 19, 2018 | Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy, Studies
Under normal circumstances, pain receptors react to painful stimuli such as burns or lacerations. Pain receptors from the body then send that information along nerves to the brain via electrical signals. Once that electrical information reaches the brain (which happens almost immediately), it is perceived as pain. This type of pain is a nociceptive pain.
Neuropathic pain, however, is different. Neuropathic pain is caused by a condition of the nerves themselves. Patients with neuropathic pain experience chronic pain without any specific injury. Neuropathic pain may be felt as a burning sensation, tingling, or a “pins and needles” sensation, or these combined. Neuropathic pain most often occurs in people with diabetes, certain vitamin deficiencies, and shingles. It may also occur after people receive certain cancer treatments following a stroke.
While it is rather simple to treat pain caused by a burn or laceration (nociceptive pain), it is very difficult to effectively treat neuropathic pain. Standard treatments for neuropathic pain include anti-epilepsy medications such as phenytoin, gabapentin, or carbamazepine and antidepressants such as venlafaxine, duloxetine, or amitriptyline. Usually, these treatments are only modestly effective. Eventually, many patients need powerful opioid medications like morphine and oxycodone to control their pain.
Researchers at the Cleveland Clinic published research that strongly suggests that stem cells may be able to improve those battling neuropathic pain. Dr. Jianguo Cheng and his research group have shown that mesenchymal stem cell transplantation into the spinal fluid can reduce pain and pain sensitivity in an animal model of neuropathic pain. In one series of experiments, they showed that mesenchymal stem cells could relieve pain in rats who had experimental nerve damage. Researchers confirmed the benefit of stem cells for neuropathic pain in several different sets of experiments. The results have been so encouraging that Dr. Cheng and the Cleveland Clinic have applied to patent the technology.
Dr. Cheng’s group also showed intravenously administered mesenchymal stem cells are just as effective as cells administered into the spinal fluid (intrathecally). This is good news for patients since it is less invasive to put stem cells into a vein than it is to infuse them into the cerebrospinal fluid. Amazingly, the research group showed that stem cells injected through either route (vein or spinal fluid) ended up finding their way to damaged nerves where they could provide maximum benefit.
While this work in animals must be performed in humans to confirm the results, this preclinical research establishes a strong foundation for those clinical studies. These results provide hope to those who struggle with daily neuropathic pain.


 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
