
by admin | Aug 27, 2018 | Adipose, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Regenerative medicine is a field of research concerned with the process of replacing diseased, dying, or dead cells with the intent of restoring structure and function. In its most basic form, regenerative medicine seeks to regrow cells that were lost or damaged due to injury or condition. Examples of regenerative medicine applications include restoring heart cells after a heart attack, repairing brain cells in Alzheimer’s disease or after stroke, or regenerating T-cells in HIV/AIDS. The potential applications of regenerative medicine are virtually limitless.
Adipose-derived stem cells hold great promise in the field of regenerative medicine. The stem cells are multipotent, which means they can become any number of cell types. For example, adipose-derived stem cells can become osteocytes (bone cells), neural cells (nerve cells), vascular endothelial cells (cells that make up blood vessels), cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells), pancreatic β-cells (cells that produce insulin), and hepatocytes (liver cells).
Adipose- or fat-derived stem cells have one obvious advantage over bone marrow cells: they are much easier to obtain. Bone marrow stem cells require an uncomfortable/painful procedure to extract them from the center of the bone. Fat-derived stem cells, on the other hand, can be taken from fat pockets in any number of places just under the skin. This essentially combines a sort of liposuction with stem cell transplantation.
Adipose-derived stem cells are the subject of nearly 200 clinical trials worldwide. Even now, fat-derived stem cells are proving useful in several clinical conditions. Adipose-derived stem cells were shown to help people after they suffered from a heart attack, by reducing the size of the damaged heart and helping to restore heart function.
Another advantage of adipose-derived stem cells is that they present possess a tri-germ lineage differentiation potential, meaning they can differentiate into all three germ layers. In other words, they have the remarkable potential to become virtually any cell in the body. This means they can be applied to more than one disease state. In neurodegenerative diseases, such as post-stroke, adipose-derived stem cells could be used to create nerve cells (neurons) and the other main type of brain cell, called glia. Both cell types are destroyed during a stroke, and both are important for proper brain function.
As more results are published from dozens of clinical trials, we will get a clearer picture of the therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stem cells. Indeed, the future of regenerative medicine is very bright.

by admin | Aug 7, 2018 | Health Awareness
Why Eat Antioxidants
Antioxidants are like bodyguards that keep our cells safe from damage that conditions and premature aging can do. They neutralize harmful free radicals present in the body. Free radicals are compounds that play a major role in Alzheimer’s, cancer, heart diseases etc.
Even though there are various supplements available in the market to fulfill your intake of antioxidants, many physicians suggest that it is more beneficial to consume them rather than take supplements. You can easily increase the daily intake of these antioxidants since they can be found in many commonly consumed foods like veggies, fruits, nuts, and sweets. Do you want to add more into your diet? Try these top foods rich in antioxidants:
Blackberries
Rich in the compound called polyphenols; berries are known to counteract the early decline of motor skills and cognitive functions that are associated with aging. Just one cup of berries provides with 7 grams of fiber, which is almost a third of the recommended daily intake.
Pecans
Only a handful of these can help lower the cholesterol levels. Pecans are highly rich in manganese, a strong anti-aging antioxidant that keeps the skin firm. For men, it is even more beneficial since it helps improve prostate health.
Cranberries
Cranberries raise the good HDL cholesterol levels and support the immune system. They are rich in an antioxidant called PAC that is responsible for keeping the bacteria from sticking to the walls of the bladder. It helps prevent urinary tract infections.
Walnuts
Walnuts are a great source of fiber, manganese, and protein. They are also rich in healthy unsaturated fats and are specifically rich in alpha-linolenic acid, a fatty acid that is commonly found in plants.
Strawberries
Loaded with skin-friendly antioxidants and rich in vitamin C, strawberries help the complexion recover from the damage caused by pollution and UV rays. They also contain high amounts of folate that protect the heart.
Artichoke
Artichokes contain magnesium which generates high amounts of energy. They also have the highest amounts of antioxidants amongst all vegetables and are also known to improve liver function and heart health.
Blueberries
Blueberries are rich in the antioxidant called anthocyanin, which is also what gives them their deep blue color. Blueberries contain high levels of vitamin K, C, and manganese which helps to fight against cancer cell growth as well as protect from heart disease memory loss due to aging.
Dark Chocolate
Dark, high-quality chocolate contains the antioxidant flavanol that reduces the risk of diabetes and lowers blood pressure. Opt for dark chocolate instead of processed, sugary chocolates as they contain higher amounts of antioxidants.
Cherries
High levels of anthocyanins give cherries their deep red color and this compound reduces inflammation and controls cholesterol. Sour, dried and canned cherries are known to have more antioxidants than fresh cherries. Tart cherries also contain melatonin which helps regulate the sleep cycle.
Raspberries
Just like the other berries, raspberries have anti-inflammatory properties which help manage arthritis and gout. The polyphenols present in their fiber helps protect against heart disease and they have a high concentration of the antioxidant, ellagitannins, which can help fight cancer.

by admin | Aug 1, 2018 | Health Awareness
Melatonin has long been hailed for its health benefits, and the more researchers study the hormone, the more its broad range of abilities is revealed. Known as “the sleep hormone,” the power of melatonin goes far beyond simply regulating sleep patterns. Scientists believe it could also play a role in managing chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes, and that it may even promote bone health and reduce obesity. Most recently, it has been discovered that melatonin could help safeguard genetic material and protect against age-related disease and health decline. Here, we take a closer look at how the hormone works to boost wellness.
A Disease-Fighting Hormone
Free radicals are chemically reactive molecules which are linked to a host of diseases, including Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. We encounter them on a daily basis, as they are found in everything from the air we breathe to medications and foods. Reducing the volume of free radicals in the body is therefore critical to preventing and managing diseases. One of the ways the body fights off free radicals is through antioxidants, the substances that counteract them.
According to research, melatonin is a potent agent in antioxidative defense. It can enter any bodily fluid or cell and actively scavenge free radicals, and it also has the ability to influence circulation. In addition to fighting free radicals, melatonin can reduce the generation of these dangerous molecules and simultaneously protect critical functions of the cells.
Research also suggests that melatonin’s ability to prevent oxidative damage, specifically in brain cells, make the substance a prime candidate for treating conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington’s disease, stroke, and brain trauma.
Where is Melatonin Found?
Melatonin was first discovered as a hormone of the pineal gland, but it is also produced elsewhere in the body. Specifically, the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a rich source of the hormone, with its tissues holding 10-100 times as much of the hormone than the blood. The GI tract also has at least 400 times more melatonin than the pineal gland.
Certain types of food are also natural sources of melatonin, including ginger, rice, bananas, barley, sweet corn, and Morello cherries. Additionally, over-the-counter melatonin supplements are available, but it is recommended that anyone considering a supplement regimen consult their doctor. Certain individuals, including women who are pregnant or breastfeeding, may not be advised to take the supplement.

by admin | Jan 31, 2017 | Studies
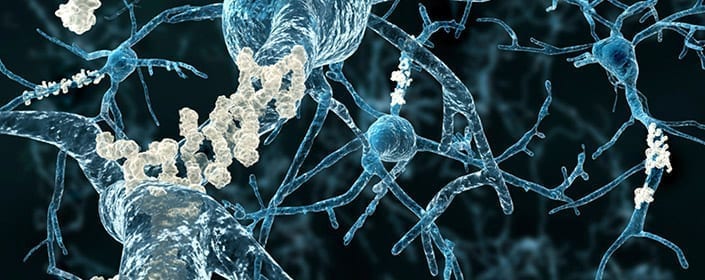
In recent years, stem cells have continued to show promise for helping combat a host of diseases, many of which relate to the brain. A recent study by Yoo-Hun Suh and colleagues has demonstrated that a specific type of stem cell could help with both the prevention and treatment of the neurodegenerative disease, Alzheimer’s.
Patients with Alzheimer’s disease lose a significant number of brain cells as a result of the disease, and the resulting damage to brain tissue is associated with cognitive and behavioral symptoms. The disease is best known for causing significant memory difficulties in its sufferers. Because stem cells offer a way to introduce new cells into the organ, they are obvious candidates for Alzheimer’s therapy.
In the current study, published in PLOS One, the researchers set out to determine if they could overcome the technical difficulty of implanting human adipose-derived stem cells into the brain and, if so, whether these cells could improve the symptoms and the physical hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease.
The researchers achieved a number of notable results. First, they showed that the stem cells were able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and migrate into the brain. Second, they demonstrated that a number of symptoms associated with Alzheimer’s disease improved with the administration of stem cells in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Specifically, learning and memory deficits were reversed. Finally, the scientists found that the administration of stem cells was associated with reductions in the physiological markers of Alzheimer’s disease – namely, the amyloid plaques in the brain that are a signature of the disease, as well as the protein that contributes to these plaques, called A. The researchers conclude that the stem cells may help with the therapy of Alzheimer’s and could potentially help with prevention as well.
That one study could achieve a technical proof-of-concept of administering the stem cells to the brain while also simultaneously demonstrating an improvement in symptoms and physiology associated with Alzheimer’s disease is incredible in terms of the potential for stem cells in aid in the therapeutic interventions of this disease.
Learn more about stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease here.
Reference
Kim, S. et al. (2012). The preventive and therapeutic effects of intravenous human adipose-derived stem cells in Alzheimer’s disease mice. PLOS One, 7(9), e45757.

by admin | Feb 3, 2016 | Stem Cell Research, Studies
More research recently published in Brain Research titled “Intravenous transplantation of bone marrow-derived mono-nuclear cells prevents memory impairment in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease.” shows how stem cell therapy may be a promising technique for preventing the cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Because of the potential for stem cell therapy to help in neurological disorders, it is already being used in clinical trials for certain afflictions, such as stroke. Here, the scientists demonstrate how the implantation of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells (BMMC‘s) can both reduce the deposits of Amyloid-β (Amyloid beta), the protein that characterizes Alzheimer’s disease, as well as improve memory in a mouse model of the disease.
“Together, our results indicate that intravenous transplantation of BMMC‘s (bone marrow-derived mono-nuclear (stem) cells) has preventive effects against the cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease model mice and suggest a potential therapeutic effect of BMMC transplantation therapy.”
Amyloid beta, which is observed in the brains of those with forms of dementia including Alzheimer’s disease, has previously been shown to lead to cognitive deficits. Many attempts to develop preventions and treatments for Alzheimer’s disease have thus targeted this specific protein. However, none of these efforts have yet been clinically successful. Our growing understanding of stem cells and their therapeutic applications has opened up a promising new avenue for Alzheimer’s disease research.
The researchers chose to specifically use BMMC‘s because of their heterogeneity and because they are relatively easy to purify and do not requiring culturing. They implanted these cells in DAL mice, which have mitochondrial dysfunction similar to that observed in Alzheimer’s disease. In these mice, BMMC‘s prevented the aggregation of Amyloid beta and led mice to perform as well as normal mice in a spatial and learning and memory task. Impressively, these effects were observed even when cognitive decline had already begun in DAL mice.
This research strongly supports the idea that stem cells could help prevent the physiological and behavioral manifestations of Alzheimer’s disease. As research moves into the clinical phase, the specific ways that stem cells can aid in dealing with this devastating disease.
Learn more about stem cell therapy for Alzheimer’s disease.
Reference
Kanamaru, T. et al. (2015). Intravenous transplantation of bone marrow-derived mononuclear cells prevents memory impairment in transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Research, 1605, 49-58.




 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
