
by Stemedix | Nov 8, 2020 | Stem Cell Therapy
More than one in seven U.S. adults is believed to have chronic kidney disease — or, roughly 15% of the population (37 million individuals). When they’re functioning properly, the kidneys remove waste from the body as well as excess fluids. In the case of patients with kidney disease, these organs become compromised and lose their ability to filter waste.
In its earliest stages, kidney disease may not present any symptoms. Over time, however, waste builds up in the blood and can lead to compounding issues, such as anemia, increased risk of heart disease, and nerve damage. When the kidneys fail, a patient must receive dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Dialysis is time-consuming and expensive. Typically, the treatment ranges in cost from $53,000 to $72,000 per year. And a kidney transplant – when a match is available – can total $400,000. Recently, however, researchers have begun exploring the potential of stem cell therapy to help kidney disease patients.
While there are several potential root causes for kidney disease, one of the most common is diabetes. In fact, 75% of patients, diabetes, or high blood pressure were the primary diagnoses, and nearly half of all patients in end-stage kidney disease have diabetes.
Treating diabetic kidney disease is challenging, because not only does the condition affect the kidneys, but it also causes systemic issues throughout the body. The condition is sometimes treated by controlling blood pressure through specific drugs, but medications for addressing the other challenges associated with diabetic kidney disease haven’t shown strong results.
Stem Cell Therapy for Kidney Disease
Regenerative Medicine, also known as stem cell therapy, has potential for those battling kidney disease. These powerful cells have anti-inflammatory properties, and can therefore help to control the widespread inflammation that takes place in diabetic kidney disease. When inflammation is controlled, the regeneration process can begin, helping to create healthy tissue and promote normal kidney functioning. Mesenchymal stem cells, in particular, appear to be especially promising for managing symptoms of kidney disease, according to early research. These cells are easily accessible and have powerful abilities to control inflammation. Clinical trials to test the efficacy of stem cells for kidney disease are ongoing. Researchers aim to understand the precise ways in which stem cells could benefit kidney disease patients, which will help inform treatment protocols. Although stem cell therapy is not a cure for kidney disease, it’s possible to help manage symptoms and may have the ability to reduce the frequency of dialysis sessions, which can ease the financial burden and time commitment for patients. Further research is needed, but some initial studies of stem cells for kidney disease shows promise in the regenerative medicine field. Contact a Care Coordinator today for a free assessment!

by admin | Nov 7, 2020 | Osteoarthritis, Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage of the joints breaks down, bone spurs form, the synovial linings become inflamed, and the ligaments around the joint calcify. All of these pathological changes combine to cause joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. The breakdown of the joint also means that it does not function properly. The arthritic joint may “lock up,” “give out,” or simply not be able to move through its normal range of motion. Early in the disease, the pain of osteoarthritis may be brought on by movement. Later, the pain is more or less constant with severe pain flares.
Initially, the treatment for osteoarthritis is pain medications, exercise, braces, and physical therapy. Joint injections may be helpful for 4 to 6 weeks, but recent research suggests that repeated steroid injections may break down cartilage and speed up joint destruction. Unlike treatments for rheumatoid arthritis, there are no disease-modifying treatments for osteoarthritis. The disease tends to get worse over time until surgery is required. Joint replacement surgery is usually the treatment of last resort.
Since osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease, a reasonable approach to therapy is to try to rebuild or regenerate the joint tissues. This would not only stop the disease progression of osteoarthritis but perhaps even heal the damaged joint. For this reason, regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy, is drawing the attention of many scientists who are looking for alternative therapeutic treatments for osteoarthritis.
Researchers tested the ability of mesenchymal stem cells to relieve pain and treat the damage of osteoarthritis. More specifically, they used the exosomes that the mesenchymal stem cells produce. Exosomes are tiny packets of substances like RNA and peptides that support tissue growth and repair. Exosomes contain most of the molecules that make mesenchymal stem cells helpful.
The scientists found that giving exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells to animal subjects with experimental osteoarthritis had some remarkable effects. Not only did the stem cell-derived treatment substantially reduce pain in the rats with osteoarthritis, but microscopic and molecular evidence also showed that the exosomes were able to repair cartilage in the affected joints. This is truly impressive when you consider that other treatments for osteoarthritis only reduce symptoms—they do not repair cartilage or stop the progression of the disease.
While this work will need to be replicated in human clinical studies (and that work has already begun), this is an exciting finding for the millions of Americans who struggle with osteoarthritis.
Reference: He, L., He, T., Xing, J. et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes protect cartilage damage and relieve knee osteoarthritis pain in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Stem Cell Res Ther 11, 276 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01781-w

by admin | Oct 30, 2020 | COPD, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung condition that makes it hard for patients to breathe. In COPD, small airways in the lungs thicken and lose their elasticity. People with COPD have shortness of breath, especially during physical activity. Patients with severe COPD may experience a more challenging quality of life. COPD patients may experience several exacerbations a year which require a stay in the hospital.
Patients with COPD typically need one or more inhalers a day. These inhalers help to open airways and, in some cases, decrease lung inflammation. Patients who also have bronchiectasis may need to take an oral antibiotic every day. During a COPD exacerbation, patients usually must receive powerful steroid treatments intravenously, routine breathing treatments, and supplemental oxygen.
People with COPD are more prone to lung infections, and so they usually receive IV antibiotics for pneumonia. Those who successfully stop smoking can help to prevent further lung damage, however, the inflammation and lung damage persists for a long time. Today, patients are seeking alternative therapies for COPD. Many are discovering regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy, that may offer an incredibly promising therapy for COPD.
The lungs have a large number of naturally occurring stem cells that can restore function. For example, mice who lose half their lung capacity from experimental COPD survive, and natural stem cells within the lungs can restore their lungs to a natural state within 5 months. Unfortunately, humans with COPD cannot repair their lungs as quickly and as fully as mice can. This is why researchers are studying the use of stem cell treatment to restore lung function in patients with COPD.
Studies have shown that stem cells have the potential to help improve lung function. Stem cell treatment improved oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, exercise tolerance, and cell injury in early studies.
One review did show that stem cell treatment is “safe and may improve patients’ condition and quality of life; however, larger-scale studies are needed to evaluate efficacy.” More research in humans is needed, but the pre-clinical (aka animal and laboratory) research in this area is quite promising.
Reference: Kokturk N, Yıldırım F, Gülhan PY, Oh YM. Stem cell therapy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. How far is it to the clinic?. Am J Stem Cells. 2018;7(3):56-71. Published 2018 Aug 1.

by Stemedix | Oct 26, 2020 | Multiple Sclerosis, Stem Cell Therapy
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic illness that damages nerves in the brain and spinal cord. In this disease, the body’s immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the myelin in the central nervous system, or the layer of insulation around the nerves. As the autoantibodies target healthy myelin tissue, neurological disabilities ensue. While there is currently no cure for MS nor any means of repairing myelin damage to improve disease progression, results from clinical trials suggest mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) could be effective in treating nerve damage caused by the condition. So many may be wondering “Can Stem Cells treat neural damage caused by Multiple Sclerosis”.
According to researchers, MSCs can help to control the immune response in people with Multiple Sclerosis. These cells have powerful self-renewal capabilities, in addition to immunomodulatory and neuroregenerative properties. While the precise cellular mechanisms of stem cells in treating Multiple Sclerosis are still being studied, researchers are encouraged by the results of several clinical trials thus far.
For instance, MSCs can be targeted to the brain tissues to reach the sites of damage, including brain lesions, to help improve the survival rate of brain cells. Also administered systemically, these cells have the potential to improve one’s quality of life and severity of symptoms.
Stem cells can be retrieved from various sources, including fat tissue, umbilical cord-derived tissue, and bone marrow aspirate. The mesenchymal stem cells derived from these tissues provide the potential power in improving cognitive function and decreasing disease severity, which is likely due to the cells’ anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective characteristics. The source of cells is determined by a few factors including age, medical history, and patient preference. Results can vary from patient to patient. Their environment factors, diet, and lifestyle choices can play an important part in the outcome. However, studies have shown that stem cell therapy for those whose immune systems have been compromised has the potential to prohibit the progression of MS for up to five years in 70% to 80% of patients. This and other stem cell treatments have the potential to significantly improve treatment outcomes for people with MS. Contact a Care Coordinator today for a free assessment!

by admin | Oct 24, 2020 | Exosomes, Osteoarthritis, Stem Cell Therapy
Osteoarthritis is a disease in which joint cartilage degenerates and the bony edges of the joint rub against each other. The disease causes pain and disability in the affected joint. There is no cure for osteoarthritis, except perhaps for artificial joint replacement surgery. Patients who are not candidates for surgery must get by with pain medications, braces, and physical therapy.
Given that osteoarthritis affects millions of people and there are limited options for long-term treatments other than major surgery, researchers are working very hard to find additional ways to manage this condition. One of the most exciting developments has been in the field of regenerative medicine, also known as stem cell therapy.
Stem cells injected into arthritic knees, for example, may help reduce the patient’s pain, protect cartilage, or even slightly heal the joint damage. Many patients feel relief and see improvements from just one therapy. Some with more advanced conditions may require a more maintenance plan. But today, researchers are now focused on the mesenchymal stem cell secretome.
What is a mesenchymal stem cell secretome? A mesenchymal stem cell secretome is the total of all of the molecules that mesenchymal stem cells secrete or release to support, restore, and regenerate tissue. The molecules released from mesenchymal stem cells, mostly through stem cell exosomes, exert many powerful benefits on joints.
From laboratory experiments in animals, we know the mesenchymal stem cell secretome is anti-apoptotic, which means it protects joint cells from committing programmed cell suicide. The secretome is also anti-fibrotic, and fibrosis can be damaging to joints and make them stiff. The secretome is pro-chondrogenic and pro-angiogenic, which means it helps build cartilage and blood vessels, respectively.
Lastly, the mesenchymal stem cell secretome modulates the immune system. While rheumatoid arthritis is considered the major inflammatory joint disease, inflammation also takes place in osteoarthritis. So, the mesenchymal stem cell secretome can modulate the immune system and reduce joint inflammation.
The main way that patients can reap the potential benefit of the mesenchymal stem cell secretome is through exosomes. Exosomes are small particles that contain most of the substances released in the secretome. Exosome treatment does not require stem cell infusions, and many, many more exosomes can be administered during a treatment session than stem cells, mainly because they are physically much smaller.
The concept of mesenchymal stem cell secretome is rather new, but it is a powerful concept in the treatment of osteoarthritis. As more human clinical studies are done, we should be able to unlock the power of the secretome for patients with osteoarthritis.
Reference: Mancuso P, Raman S, Glynn A, Barry F, Murphy JM. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Osteoarthritis: The Critical Role of the Cell Secretome. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:9. Published 2019 Jan 29. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2019.00009

by Stemedix | Oct 19, 2020 | Stem Cell Therapy, Pain Management
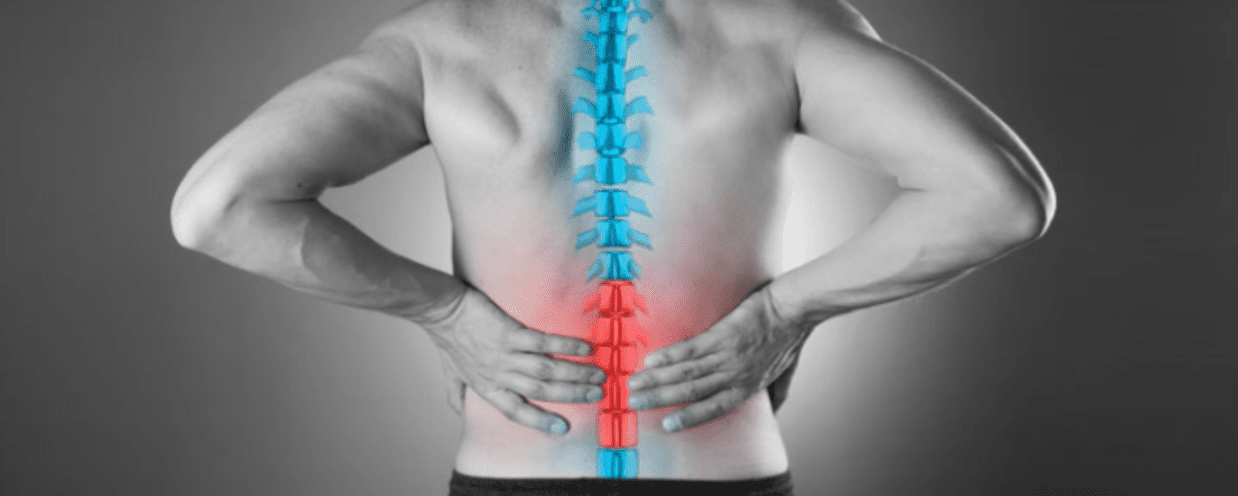
Half of all working adults in the U.S. report back pain symptoms each year. In many cases, the issue is acute and will resolve over time. In other cases, the pain can be pronounced and intensify if left unaddressed, interfering with daily activities. Understandably, many patients hope to avoid invasive back surgeries but are still seeking relief through other means. When conventional therapies fall short, stem cell therapy could be a solution for you.
Stem Cell Therapy as a Back-Pain Treatment
Existing treatments for many conditions causing pain in the back include anti-inflammatory and prescription pain medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. When pain is severe, more invasive approaches, including surgical spinal fusion, may be recommended. Unfortunately, pain can persist even after surgery.
Today, patients have an alternative minimally invasive option. Stem cell therapy is being leveraged to improve lower back pain to do some of the following:
- Repair disc or facet joint damage
- Improve function
- Alleviate chronic pain
The treatment has been implemented for a number of back conditions, including degenerative disc disease, spinal cord injury, herniated discs, sciatica, and spinal facet disease. The stem cells can be strategically administered with the goal of restoring structural integrity, function, and pain reduction.
With spinal facet disease, the stem cells can be directed to the cartilage surrounding the spinal facet joints to reduce pain and inflammation and improve mobility. The injection is performed via x-ray guidance for the utmost level of precision.
If you’re experiencing pain from disc or facet injuries caused by arthritis, overuse, or trauma, you could potentially be an ideal candidate for stem cell therapy for back pain. The treatment is widely considered to be safe and effective, and in addition to being minimally invasive, requires little recovery time before yielding improvements. Contact a Care Coordinator today for a free assessment!

 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
