
by admin | Mar 6, 2019 | Health Awareness
Stress is the body’s natural response to a threat, but when this response occurs often and even when there is no real danger present, it can increase your risk of developing serious illnesses. Moreover, both chronic and short-term stress can affect the body. Here, we take a closer look at how being stressed out impacts your health.
How Stress Works
When you become stressed, your heart rate becomes elevated and your blood pressure spikes. The stress hormone cortisol is also released, which send the body into “fight or flight” mode. Breathing becomes more rapid, and the muscles tense to prepare for action. While this response served our ancestors well in precarious situations, the effects of being in this state consistently can be harmful.
Symptoms of Stress
Stress produces a number of physical effects, including chest pain, fatigue, stomach upset, difficulty sleeping and focusing, and headaches. It’s also linked to heartburn, lower sex drive, and reproductive issues in women.
Of course, stress doesn’t just impact the physical realm. It can also alter your mood, leading to irritability or anger, lack of motivation, restlessness, and ultimately, sadness or depression. These affects can manifest through behavioral factors, too. Stressed individuals may be more likely to engage in dangerous behaviors, such as drug or tobacco use and alcohol abuse. Angry outbursts, over- or undereating, lack of exercise, and social withdrawal are also common behavioral effects.
The Serious Nature of Chronic Stress
Beyond contributing to the unfavorable conditions listed above, stress can also put you at risk for concerning conditions, including heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. Studies show that chronic stress is linked with inflammation, which is thought to be a culprit behind many chronic illnesses, including diabetes, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis. It’s suspected that stress is related to an increase in cytokines, pro-inflammatory cells which are typically used for defense against infection. When they are triggered without an infection, however, the immune system attacks itself, leading to autoimmune conditions.
How to Combat Stress
Luckily, there are many practical ways to address stress, alleviate inflammation, and lower cytokines to support better overall health. While relaxation techniques such as meditation are preferred among many individuals, others find counseling to be helpful in identifying the sources of stress and developing healthy coping mechanisms. Exercising regularly, setting aside time for personal interests, and socializing regularly can also help to alleviate tension.

by admin | Mar 4, 2019 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. In fact, when people casually use the term “arthritis” or think of the arthritis of old-age, they are usually talking about osteoarthritis. People with arthritis experience many symptoms in and around the affected joints including pain and swelling. The affected joints may become unstable or “give out.” At the same time, people who suffer from osteoarthritis may not be able to move their joints fully or smoothly. Commonly people feel that their joints are “stiff.”
Early in osteoarthritis, the pain may just occur occasionally. Perhaps, the person feels sharp pain when moving a certain way. In later stages of osteoarthritis, the affected joints constantly ache, and moving the joint becomes intensely painful.
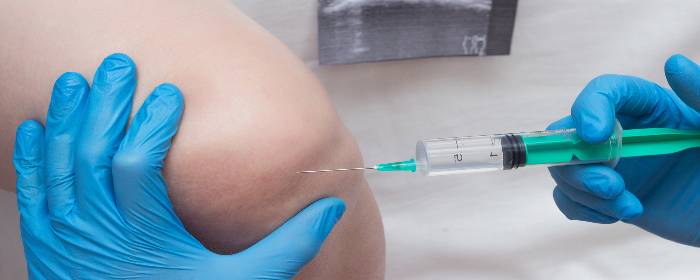
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs can help in some cases, but they become less effective as osteoarthritis becomes more severe. Often people with osteoarthritis must receive injections of anesthetics and steroids into the joints itself. Ultimately, patients often need orthopedic surgery to grind away diseased joint tissue or even replace the joint with the artificial one.
Researchers are searching for ways to reverse osteoarthritis instead of just treating the symptoms. Fortunately, stem cells may offer hope. Doctors have long known that in people with osteoarthritis, the cartilage becomes thin and breaks down. Joint cartilage lubricates the joint, acts as a shock absorber, and helps the joint move smoothly. When cartilage breaks down, the joint becomes stiff, painful, and irritated. As recent research suggests, mesenchymal stem cells may rebuild and restore joint cartilage.
Two scientists, Kristjánsson and Honsawek, recently reviewed the state of the research in this field. They identified eight clinical studies that tested mesenchymal stem cells on patients with varying degrees of osteoarthritis. The clinical trials demonstrated several intriguing findings. Most notably, mesenchymal stem cells were able to promote cartilage regeneration, reduce pain, and improve joint function. The scientists also found that the more stem cells that were injected, the better the outcome. In addition, the beneficial effect of stem cells occurred whether the cells were taken from the patient (autologous stem cells) or from young, healthy donors (allogenic stem cells).
Importantly, patients with mild to moderate osteoarthritis enjoy the greatest apparent benefit from stem cell injections. This suggests that doctors and patients should consider stem cell treatment earlier in the course of osteoarthritis before joints become too damaged and likely require surgery.
Mesenchymal stem cell injection for osteoarthritis has now been tested in at least eight clinical studies including randomized clinical trials, which are the gold standard studies for evaluating treatments in medicine. Research is ongoing and still needed but these results are strongly encouraging. They may offer, for the first time, a way for patients to reverse the changes of osteoarthritis rather than simply treating the symptoms of the disease.
Reference: Kristjánsson et al. (2017). Mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. World Journal of Orthopedics. 2017 Sep 18; 8(9): 674–680.

by admin | Mar 3, 2019 | Health Awareness
Experts have known for many years now that certain nutrients play an important role in preserving cognitive function. Brain-healthy foods like blueberries, nuts rich in omega-3 fats and seeds, and many types of vegetables have been hailed for their ability to support mental acuity. Now, sage extract is emerging as a serious contender in the fight against cognitive decline. Discover how this powerful supplement is improving brain health across various populations below.
The Decline of Acetylcholine
In both normal age-related cognitive dysfunction and dementia, the neurotransmitter acetylcholine declines. Neurotransmitters have a critically important role in brain function, as they allow brain cells to communicate with each other. Acetylcholine is among the most plentiful and important neurotransmitters, as it supports attention, memory, learning, and reasoning. It is also impacted most severely in Alzheimer’s disease. In trials conducted on patients with Alzheimer’s disease, treatments used specifically to boost acetylcholine were linked to a 20% lower mortality. Sage extract, it appears, is among the treatments which can support this essential neurotransmitter.
How Sage Helps
In recent studies, a proprietary sage extract with unique properties has been shown to boost cognitive performance and cerebral blood flow, in addition to improved longevity. It also protects acetylcholine by blocking an enzyme which depletes it. This distinct extract exhibits superior biological activity, has a chemical fingerprint unlike any other form of sage, and has been rigorously tested. In a study conducted in adults over the age of 64, the sage extract:
- Improved memory performance by 60%, compared to placebo subjects
- Led to attention scores 2.5x greater than those of placebo subjects
- Improved brain function within a matter of hours
In a separate study, the extract also improved neuropsychiatric symptoms in people with Alzheimer’s: cognition scores improved by 26% in the group that was given the sage extract, whereas the placebo group’s scores declined by 22%. Interestingly, the powerful treatment even improved mood and cognition in younger individuals, showing results such as reduced anxiety and fatigue, extended memory and attention and boosted mood.
In addition to improving present cognitive function, sage is also believed to help combat future age-related impairment. This is because the extract supports neurotrophins, the proteins which support brain function by replenishing and repairing brain cells.
While some types of sage extracts are available for purchase, it’s important to remember that concentrated forms of any herb or supplement can have intensified effects and should therefore only be taken under the care of a physician. In the meantime, adding the herb to foods like poultry, sweet potatoes, and pork is an effective way to flavor your meals without adding extra calories, and it may deliver some brain-boosting benefits at the same time.

by admin | Mar 1, 2019 | Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Osteoarthritis, Stem Cell Therapy, Studies
Cartilage plays several important roles in the way joints move and function. Joint cartilage provides lubrication, acts as a shock absorber, and helps the joint move smoothly. Joint cartilage is comprised of two substances chondrocytes (i.e. cartilage cells) and extracellular matrix (proteins such as hyaluronic acid, collagen, fibronectin, etc.).
Many conditions can lead to joint cartilage defects. In young people, the most common cause of the joint cartilage defect is an injury. For instance, a football player suffers a hard contact that injures the joint. Another example is a gymnast who repeatedly places substantial impact forces on the knee and other joints of the lower body, resulting in damage. In older people, the most common cause of joint cartilage defects is Osteoarthritis. Over time, the joint cartilage breaks down in the cartilage loses its ability to lubricate, absorb shock, and support the smooth movement of the joint. This leads to stiffness, pain, and “trick” joints, among other symptoms.
Orthopedic surgeons, rheumatologists, and other physicians have attempted to treat these conditions by injecting the damaged joint with one of the two main components of joint cartilage: extracellular matrix. Physicians inject hyaluronic acid (and sometimes related extracellular matrix proteins) to help replace and restore damaged joints. This approach can be helpful for some patients, but it is certainly not a cure.
Only recently, have researchers attempted to replace the other component of joint cartilage: chondrocytes. Specifically, researchers have focused their efforts on mesenchymal stem cells that have the ability to differentiate and become cartilage cells. Li and colleagues injected combinations of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronic acid into animals with experimental cartilage defects. They showed that hyaluronic acid injections alone modestly repaired the cartilage damage. However, when stem cells plus hyaluronic acid was injected, the joints were almost completely repaired. In other words, stem cells plus hyaluronic acid resulted in much greater improvement in joint cartilage damage than hyaluronic acid alone.
The authors of the study concluded that “bone marrow stem cells plus hyaluronic acid could be a better way to repair cartilage defects.” While additional work is needed, these results are extremely exciting for people who suffer from joint cartilage defects such as osteoarthritis. In the future, people who are candidates for hyaluronic acid injection treatments may instead receive a combination of hyaluronic acid plus stem cells and may enjoy an even greater benefit than hyaluronic acid treatment alone.
Reference: Li et al. (2018). Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Combination with Hyaluronic Acid for Articular Cartilage Defects. Scientific Reports. 2018; 8: 9900.

by admin | Feb 28, 2019 | Health Awareness
We’re told since childhood that we need vitamins to stay strong, but just how significant a role does each nutrient really play in our wellness? Specifically, you may have heard about the importance of getting ample vitamin C to fight off illness, but what does it really do to keep us healthy? Let’s take a closer look at the significance of vitamin C, and how you can make sure you’re getting enough.
Why Our Health Depends on Vitamin C
Vitamin C supports a number of key bodily functions. It helps to produce L-carnitine and some neurotransmitters, and it also has antioxidant activity which could help to decrease the risk of certain cancers. It also aids in iron absorption.
Moreover, vitamin C plays an important role in collagen production. Collagen is found in connective tissue and is the most abundant protein found in mammals. It makes up tendons, ligaments, cartilage, skin, bones, blood vessels, and more. Without enough vitamin C, collagen production may become compromised. This means wounds may take longer to heal, as research shows vitamin C can help form scar tissue.
Researchers have also found that vitamin C can attack drug-resistant strains of tuberculosis and that in general, people with sufficient levels of the vitamin may be more likely to fight off infections than those without. Additionally, individuals who contract colds and have enough of the nutrient may experience shorter periods of illness and milder symptoms. High doses have even been proven to benefit cancer patients by stopping the growth and potentially even killing off cancer cells.
Without enough vitamin C, you may notice symptoms of a deficiency, including nosebleeds, a slowed metabolism, weakened tooth enamel, painful joints, bleeding gums, anemia, easy bruising, and dry or splitting hair. A severe deficiency is known as scurvy, but this condition is typically experienced only by malnourished, older adults.
How to Get Plenty of Vitamin C
Vitamins can either be fat soluble or water soluble. Vitamin C falls into the latter category, which means it isn’t stored by the body, and any excess amount will be released through urine. Because we don’t build up a supply of it, it’s critically important that we get enough through diet.
The daily recommended amount for vitamin C is 65 to 90 mg for adults, but these levels may be different for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. To take in more vitamin C through your diet, snack on fruits like cantaloupe, pineapple, strawberries, citrus fruits, and watermelon. Veggies like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, peppers, spinach, and sweet potatoes are also rich in the nutrient. If you’re concerned about your intake, consider speaking with your doctor to determine whether you might be a good candidate for a daily supplement.




 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
