
by admin | Sep 5, 2018 | Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy, Studies, Traumatic Brain Injury
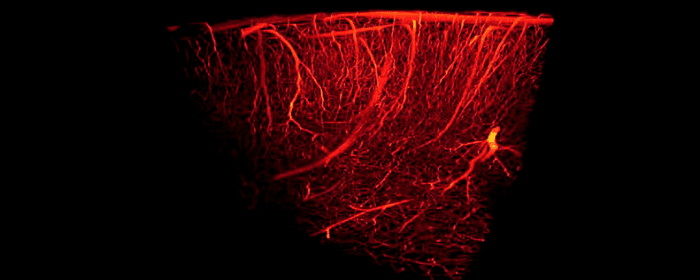
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is one of the most common causes of disability in the United States, affecting over 13 million citizens. Traumatic brain injury is responsible for over 2 million emergency department visits, over a quarter of 1 million hospitalizations, and nearly 60,000 deaths each year.
Traumatic brain injury harms brain tissue in two phases. The first phase of injury occurs at the time of the traumatic incident. This initial injury may cause small or large areas of the brain to bleed. It may also shear (stretch/tear) nerve cells, making them dysfunctional. The second phase occurs hours or days after the initial injury. The brain is subjected to ongoing damage because of inflammation, cell death, and injury to blood vessels. Many people with TBI are left with lifelong problems with thinking, memory, and behavior.
In both of these phases of injury, one major way to help prevent long-term brain damage is by maintaining adequate blood flow to brain tissue. Unfortunately, once the damage has occurred, it can be a challenge to reverse the damage. Patients usually must endure months or years of physical and occupational therapy to regain what was lost. Moreover, patients often need substantial amounts of psychiatric and psychological support to treat mental health problems.
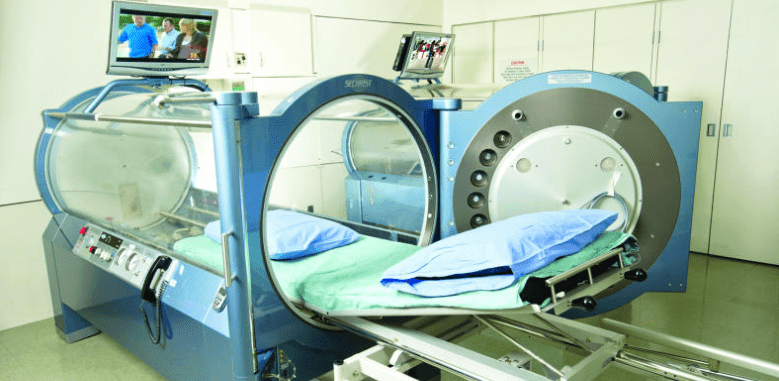
Fortunately, researchers are using hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) to improve blood flow to the brain in patients with traumatic brain injury. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy provides patients with pure oxygen (100%) at slightly higher pressures than they would experience normally. It is been used for hundreds of years to treat scuba divers who suffered “the bends” or decompression sickness; however, researchers are finding that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a “coveted neurotherapeutic method for brain repair.”
To study the effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy, researchers selected 10 people who had suffered mild traumatic brain injury in the previous 7 to 13 years. Patients all had brain damage that interfered with attention, memory, and thinking abilities.
Even though patients had sustained traumatic brain injury and brain damage a decade earlier, hyperbaric oxygen therapy was able to improve blood flow in the brain. Likewise, the amount of blood detected within the brain significantly increased, suggesting that hyperbaric oxygen therapy actually caused blood vessels in the brain to grow and multiply. Just as impressively, patients with chronic brain damage performed better on tests of cognition (i.e. thinking). They were able to process information more quickly, they had better motor function, and they were able to take in and process information about the world around them more efficiently.
Because people with traumatic brain damage have limited treatment options to improve their situations, these results are incredibly exciting. This was a study on 10 patients and more studies on larger numbers are still needed to build on these findings. Nonetheless, these results are quite encouraging for people with traumatic brain injury and their loved ones.

by admin | Aug 28, 2018 | Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
The evidence for the promise of mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine has been growing for several years. With new sources regularly emerging, stem cells can come from a large variety of sources. Postnatal mesenchymal stem cells appear to have the most promise in regeneration. A new review has addressed how mesenchymal stem cells can be used with innovative scaffolding engineering approaches to improve techniques in regenerative medicine.
Mesenchymal stem cells are, on their own, good candidates for regeneration because of a number of characteristic features. For instance, they can differentiate into many different types of cells. Osteoblasts and chondroblasts are two cell types that mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into and that can be supported in bone regeneration by 3D-printed biomaterials like scaffolds.
Mesenchymal stem cells also can have beneficial impacts on the immune system. Unlike with other stem cell types, the severe immune reactions that may occur with the transplantation of foreign materials into the body can often be avoided with the use of mesenchymal stem cells, making them a safe option in regenerative medicine.
The current review addresses the ways in which bone regeneration can be optimized through the use of mesenchymal stem cells and scaffold engineering and how new concepts in bioengineering may be able to improve regenerative medicine in combination with mesenchymal stem cell approaches. Future research will need to focus on how we can customize regenerative approaches using what we know about mesenchymal stem cells and the most cutting-edge innovations in bioengineering.

by admin | Aug 21, 2018 | Stem Cell Therapy, Wharton's Jelly
Mesenchymal stem cells have been showing promise in the treatment of a variety of diseases and injuries. These cells are derived from different tissue types, and it appears that where the stem cells come from is indicative of how they function and how appropriate they are for use in different applications. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells have been deeply studied and are often considered a go-to for stem cell research and clinical use.
However, there are several limitations that bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells pose, particularly from a practicality standpoint, and thus, researchers have begun to try to understand how other types of stem cells may achieve similar or better results than those from the bone marrow. A recent review, published in Act Histochemical, compiled comprehensive data on the biological properties associated with a specific type of mesenchymal stem cell called Wharton’s Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
These stem cells, which come from the umbilical cord, are able to differentiate into mature cells that make up several different types of tissues and can even turn into non-mesenchymal cells, such as neurons, or brain cells. They are useful in that they spontaneously move to sites of injury or inflammation and may, therefore, be able to help restore tissue and normal functioning. They are also unlikely to instigate adverse immune system reactions.
While it is advantageous that bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells have been studied extensively and therefore are associated with broad knowledge of therapeutic applicability, the cells are difficult to isolate and use. In contract, cells from the umbilical cord matrix, or Wharton’s jelly, are easy to isolate and also appear to be good candidates for therapeutic intervention. Future research should therefore look more closely at how Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells can be used to treat disease and injury. As noted by the authors of this review, there are specifically dysfunctions of the central and peripheral nervous system that these stem cells may be able to address.

by admin | Aug 10, 2018 | Bone Marrow, Wharton's Jelly
Mesenchymal stem cells that come from different cell sources can look similar but behave differently. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells tend to be the gold standard for isolating and using mesenchymal stem cells, it is not particularly easy to access these cells from the bone marrow. Because there are other, much more easily accessible mesenchymal stem cells, such as those from the umbilical cord, it is important to establish the differences between the different types of stem cells so that each can be used when most appropriate and when most advantageous.
One important difference is how to isolate the cells and how easy it is to do so. Recent work published this year in Stem Cells and Development helped to define the best way to isolate mesenchymal stem cells from the Wharton’s jelly of umbilical cords. The researchers also looked at the gene expression profile and the immune system characteristics of both bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
The researchers found that mesenchymal stem cells that came from the Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord had a better capacity to expand into more tissue than those taken from the bone marrow. Further, their gene expression was different. In the stem cells from the Wharton’s jelly, there was greater gene enrichment for genes related to cell adhesion, proliferation, and immune system functioning than in the cells from the bone marrow. These cells also induced the maturation of brain cells more so than did the mesenchymal stem cell derived from bone marrow.
These results show that Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells have distinct properties from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and likely have specific advantages as well to help treat those battling osteoarthritis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and other degenerative conditions. Further research will help bear out more of the differences between these types of stem cells and how each type can best be used to help patients.

by admin | Aug 2, 2018 | Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy, Studies
While most approaches to stem therapy involve infusing purified stem cells into the body, Thom and fellow researchers have shown that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is capable of stimulating the body to produce its own stem cells. Thom, Heyboer, and co-authors have extended this work by showing that by slightly increasing the pressures used during hyperbaric oxygen therapy, one can significantly increase the number of stem cells produced.
In his original work, Thom and colleagues showed that a single, two-hour session of 2.0 atmospheres (atm) pressure (twice the air pressure we normally feel at sea level) was capable of doubling the number of stem cells in the bloodstream. Twenty treatments increased stem cell levels by 800%. To study this phenomenon more closely, Thom’s research group recruited 20 patients to undergo hyperbaric oxygen treatment, some at the original 2.0 atm pressure, and some at 2.5 atm. The primary goal of this research was to find out whether a higher pressure was capable of eliciting a greater number of cells.
As before, treatment with 2.0 atm of hyperbaric oxygen substantially increased the number of stem cells found in the blood. However, treatment with 2.5 atm doubled or even tripled the number of stem cells produced compared to the 2.0 atm treatment session. In other words, a slightly higher pressure causes the body to produce substantially more of its own stem cells.
Researchers focused on two types of stem cells, in particular, CD34+ and CD45-dim—markers that appear on stem cells and/or progenitor cells. They are primarily found on cells in the bone marrow. Stem cells with CD45-dim generally go on to become bone, blood, or blood vessel cells, while CD34+ cells can differentiate into almost any cell. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is thought to stimulate the bone marrow to produce and release these stem cells into the bloodstream, which is the reason these treatments raise stem cell levels in the blood.
The results published by Thom and coworkers suggest that patients who wish to enhance the number of stem cells should consider undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Furthermore, the greatest number of stem cells was observed after 20 treatment sessions, suggesting that a greater effect occurs with more treatments.

 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
