Understanding Long-Term Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury and How Regenerative Medicine Can Help
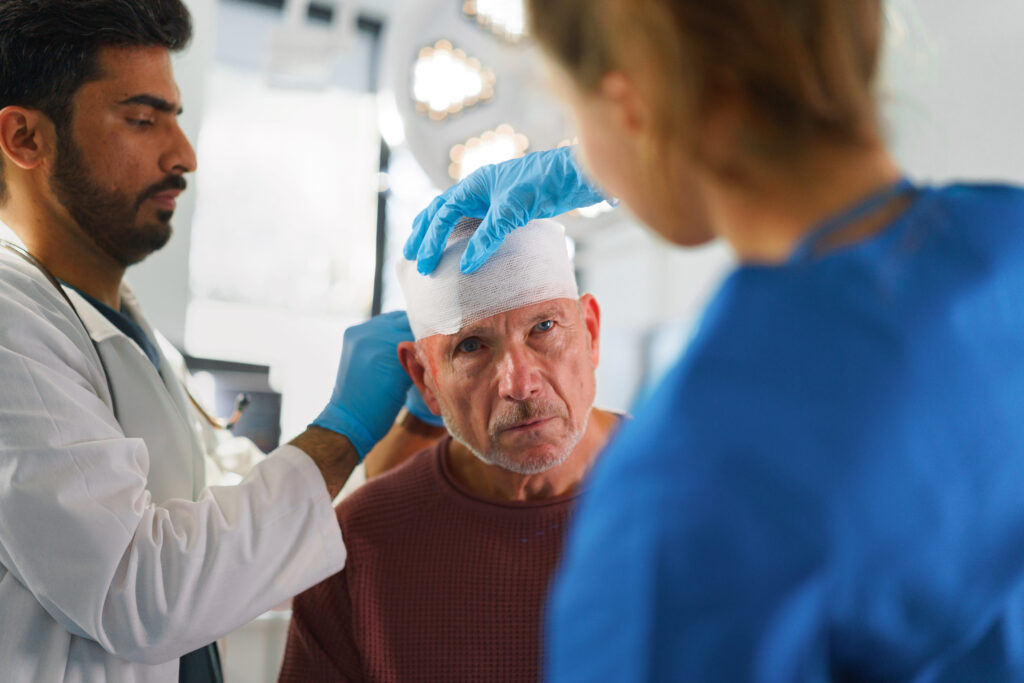
Traumatic brain injury can lead to lasting changes in your physical abilities, thinking, and emotions. You may notice that some symptoms improve with time, while others persist for months or even years. Identifying the range of symptoms of TBI is an important step in managing daily life and planning ongoing care. At Stemedix, we work…