
by admin | Aug 14, 2018 | Bone Marrow, Stem Cell Research
Colitis is inflammation of the colon, also known as the large intestine. Several things can cause colitis such as infection, medication, ischemia, or chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Inflammatory bowel diseases that affect the colon, such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, are particularly challenging for patients. It is a chronic disease that causes cramping pain, bloody diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and many other chronic, challenging symptoms.
Since ulcerative colitis does not occur naturally in animals, researchers sometimes use an experimental form of colitis to mimic the disease seen in humans. This experimental colitis serves as a model to investigate treatments for inflammatory bowel disease. Essentially, researchers create a situation in which mice develop a condition that looks very much like ulcerative colitis. They develop inflammation in the large intestine, along with signs of oxidative stress and cell death. Conversely, treatments for ulcerative colitis reduce or prevent inflammation, oxidative stress, and cell death in the colon of these experimental mice.
Researchers used this model of experimental colitis to study the effect of bone marrow stem cells as a treatment for colitis. More specifically, they tested the effects of a certain part of bone marrow stem cells called extracellular vesicles. Extracellular vesicles are small spheres that containing various beneficial substances. Stem cells release these vesicles into the body. A single stem cell can release hundreds of extracellular vesicles. In fact, it is the extracellular vesicles that are believed to contain many of the useful substances that are released by bone marrow stem cells such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These substances can precisely target sick and damaged cells in the body and repair them.
Impressively, when researchers used extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow stem cells to treat animals with experimental colitis, they observed rather extraordinary results. These vesicles protected the intestines from colitis damage. Untreated animals had severely damaged intestines when viewed under a microscope, but animals treated with extracellular vesicles had nearly normal looking intestines. Treatment also substantially reduced levels of cytokines related to oxidative stress, such as IL-1β. Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow stem cells also apparently blocked the intestinal cells’ ability to undergo cell suicide (apoptosis).
Taken together, these results strongly suggest that mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, specifically the extracellular vesicles contained within them, can dramatically improve experimental colitis. While more research is needed, this study suggests that these stem cell products could one day be a useful treatment for inflammatory bowel diseases, such as ulcerative colitis and inflammatory bowel disease.

by admin | Aug 10, 2018 | Bone Marrow, Wharton's Jelly
Mesenchymal stem cells that come from different cell sources can look similar but behave differently. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells tend to be the gold standard for isolating and using mesenchymal stem cells, it is not particularly easy to access these cells from the bone marrow. Because there are other, much more easily accessible mesenchymal stem cells, such as those from the umbilical cord, it is important to establish the differences between the different types of stem cells so that each can be used when most appropriate and when most advantageous.
One important difference is how to isolate the cells and how easy it is to do so. Recent work published this year in Stem Cells and Development helped to define the best way to isolate mesenchymal stem cells from the Wharton’s jelly of umbilical cords. The researchers also looked at the gene expression profile and the immune system characteristics of both bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells.
The researchers found that mesenchymal stem cells that came from the Wharton’s jelly of the umbilical cord had a better capacity to expand into more tissue than those taken from the bone marrow. Further, their gene expression was different. In the stem cells from the Wharton’s jelly, there was greater gene enrichment for genes related to cell adhesion, proliferation, and immune system functioning than in the cells from the bone marrow. These cells also induced the maturation of brain cells more so than did the mesenchymal stem cell derived from bone marrow.
These results show that Wharton’s jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells have distinct properties from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and likely have specific advantages as well to help treat those battling osteoarthritis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and other degenerative conditions. Further research will help bear out more of the differences between these types of stem cells and how each type can best be used to help patients.

by admin | Aug 2, 2018 | Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy, Studies
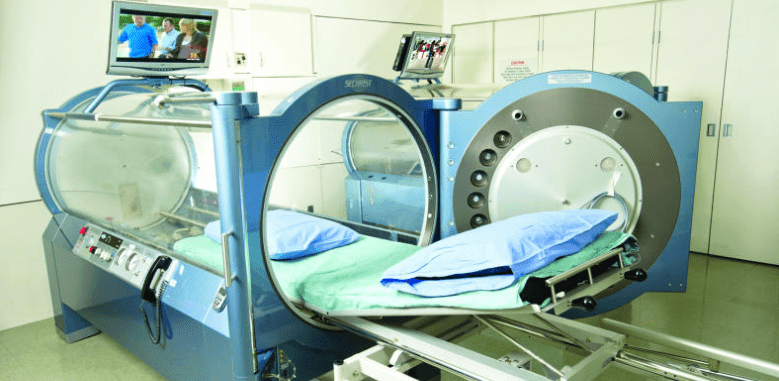
While most approaches to stem therapy involve infusing purified stem cells into the body, Thom and fellow researchers have shown that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is capable of stimulating the body to produce its own stem cells. Thom, Heyboer, and co-authors have extended this work by showing that by slightly increasing the pressures used during hyperbaric oxygen therapy, one can significantly increase the number of stem cells produced.
In his original work, Thom and colleagues showed that a single, two-hour session of 2.0 atmospheres (atm) pressure (twice the air pressure we normally feel at sea level) was capable of doubling the number of stem cells in the bloodstream. Twenty treatments increased stem cell levels by 800%. To study this phenomenon more closely, Thom’s research group recruited 20 patients to undergo hyperbaric oxygen treatment, some at the original 2.0 atm pressure, and some at 2.5 atm. The primary goal of this research was to find out whether a higher pressure was capable of eliciting a greater number of cells.
As before, treatment with 2.0 atm of hyperbaric oxygen substantially increased the number of stem cells found in the blood. However, treatment with 2.5 atm doubled or even tripled the number of stem cells produced compared to the 2.0 atm treatment session. In other words, a slightly higher pressure causes the body to produce substantially more of its own stem cells.
Researchers focused on two types of stem cells, in particular, CD34+ and CD45-dim—markers that appear on stem cells and/or progenitor cells. They are primarily found on cells in the bone marrow. Stem cells with CD45-dim generally go on to become bone, blood, or blood vessel cells, while CD34+ cells can differentiate into almost any cell. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is thought to stimulate the bone marrow to produce and release these stem cells into the bloodstream, which is the reason these treatments raise stem cell levels in the blood.
The results published by Thom and coworkers suggest that patients who wish to enhance the number of stem cells should consider undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Furthermore, the greatest number of stem cells was observed after 20 treatment sessions, suggesting that a greater effect occurs with more treatments.

by admin | Jul 26, 2018 | Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
As patients start to investigate the many different types of stem cells, it can become overwhelming. Often stem cells are organized into groups by tissue source, i.e., by the type of tissue stem were derived. While it can be important to know whether stem cells come from adipose tissue (fat cells) or the umbilical cord, for example, it is equally important to understand the types of stem cells by their capacity to differentiate. In other words, what are the types of stem cells organized by their ability to become different or more mature cells?
One of the most intriguing features of stem cells is their ability to become virtually any other type of cell. We all start out as a sperm and an egg but end up as an exquisitely organized collection of heart cells and brain cells and kidney cells, etc. At each step of the way—from early cells to the adult human body—stem cells become more differentiated and less capable of becoming any other cell. Thinking about them this way, stem cells are grouped into four categories:
- Omnipotent stem cells
- Pluripotent stem cells
- Multipotent stem cells
- Unipotent stem cells
Omnipotent stem cells
Omnipotent stem cells, also called totipotent stem cells, truly have the capacity to become any other cell. Omnipotent stem cells can become embryonic cells or even the cells that support the embryo, like the placenta. A fertilized egg is an example of an omnipotent cell. While omnipotent/totipotent stem cells are potentially incredibly useful, their use is highly restricted and controversial. As such, they are not usually used for therapeutic purposes, or even for research.
Pluripotent stem cells
Pluripotent stem cells are the next best thing to omnipotent stem cells. Pluripotent stem cells can become nearly any tissue in the body. Like omnipotent stem cells, the use of naturally occurring pluripotent stem cells is also controversial because they require the use of embryos. However, researchers have devised a rather ingenious way to take regular cells and turn them into pluripotent stem cells. These stem cells are referred to as induced pluripotent stem cells or iPSCs. Induced pluripotent stem cells are particularly exciting because of their potential as research tools and clinical therapeutics. Most importantly, iPSCs sidestep controversy because they are made from mature cells.
Multipotent stem cells
Multipotent stem cells can become any number of mature cells. For example, a mesenchymal stem cell can become a muscle cell or fat cell, a bone cell or cartilage cell. Another powerful feature of multipotent stem cells is that they can divide and form other multipotent stem cells. Thus, their ability to differentiate and self-renew makes them incredibly versatile for research and clinical purposes.
Another example of multipotent stem cells is the type of cells that give rise to blood cells, namely hematopoietic stem cells. Hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into myeloid type or lymphoid type, but once they do, they are restricted to become their corresponding type of blood cell. For example, myeloid cells can become red blood cells or certain white blood cells, while lymphoid cells are more or less destined to become lymphocytes.
Unipotent stem cells
Unipotent stem cells are technically stem cells but have very little potential become anything other than the one cell they were destined to become. For example, a cartilage stem cell is destined to become a cartilage cell, while a bone stem cell is destined to become a bone cell. A mesenchymal stem cell could become either one, but by the time it has differentiated into a cartilage or bone stem cell, its fate is essentially predetermined. As you may expect, unipotent stem cells have limited clinical usefulness.
In summary, as you think about different types of stem cells, it can be important to think about where the stem cell came from (e.g. fat tissue), but also consider its potential for self-renewal and differentiation.

by admin | Jul 25, 2018 | Bone Marrow, Health Awareness, Stem Cell Research, Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cells derived from bone marrow, or hematopoietic stem cells, are a topic of significant debate in the medical community. While they have exhibited significant potential for benefiting people with both cancerous and noncancerous diseases including immune deficiencies, not all methods for administering bone marrow are created equal. While intra-articular injections of bone marrow are more common and considered safer, intravenous methods pose serious risks, which are explored here.
Intra-articular injections involve injecting bone marrow directly into the compromised joint, whereas intravenous methods entail infusing bone marrow stem cells into the body through the veins. Intra-articular injections have shown promise in treating conditions such as osteoarthritis (OA) in joints such as the knee and has proven to achieve pain relief for moderate-to-severe cases of osteoarthritis.
Intra-articular treatments are localized, so the injected bone marrow is already in its target location upon being administered. According to research, this form of therapy is generally considered to be safe. In intravenous bone marrow transplants, however, there are serious risks associated with treatment. Bacterial infections are common, while viral and fungal infections can also occur and cause life-threatening conditions, such as organ failure.
Risk factors for developing any complication associated with intravenous bone marrow transplantations vary based on a number of factors, including the patient’s age, genetics, and type of disease being treated. With that said, due to its limited risks, intra-articular bone marrow methods appear to be the safest form of treatment currently available. Although each patient will need to discuss risk factors alongside potential benefits with his or her physician, oftentimes the risks appear to outweigh the potential benefits.
There are alternative therapies with fewer potential side effects which may be explored such as Adipose and Umbilical Cord-derived stem cells. These regenerative medicine treatments not only can treat osteoarthritis and sports-related injury conditions, but have also shown positive results in treating neurological conditions such as Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Post-Stroke, and Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI).

 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
