Parkinson’s Disease Doctor
There is no specific test for diagnosing Parkinson’s at this time. Neurologists are doctors who specialize in conditions of the nervous system. Parkinson’s disease is diagnosed based on medical history, a review of symptoms, and a neurological exam.
Your healthcare provider may recommend a specific scan known as a Dopamine Transporter (DAT) scan. This can be used to confirm the suspicion of Parkinson’s, but ultimately, it is the results of your neurological exam and symptoms that determine the diagnosis. Most people don’t require a DAT scan.
NEW! Now accepting Medicare
Your Medical Treatment Team
Your healthcare team may order laboratory tests, such as blood tests, to rule out any other conditions that could be causing symptoms. Imaging tests, such as an MRI, ultrasound of the brain, and PET scans, can also be used to rule out other disorders. However, imaging tests are not helpful in diagnosing Parkinson’s disease.
A member of your healthcare team will examine you and may prescribe carbidopa/levodopa, also known as Rytary, Sinemet, or other Parkinson’s disease medicines. It is important to receive a high dose of the drug, as low doses are not reliable. This medicine can often confirm the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease.


Understanding Parkinsons’s Diseases
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease can be a time-consuming process. It is advisable to schedule regular follow-up appointments for evaluation by neurologists who specialize in movement disorders. They can then make a Parkinson’s diagnosis.
A new test might be on the horizon. Researchers are currently developing a test for Parkinson’s disease that can identify symptoms before they manifest. This test is referred to as an alpha-synuclein seed-amplification assay. In 2023, researchers examined the spinal fluid of over 1,000 individuals to identify clumps containing the alpha-synuclein protein, which is also found in Lewy bodies. These clumps, which the body struggles to break down, contribute to the damage of brain cells.
Clusters of alpha-synuclein are a distinctive hallmark of Parkinson’s. The test accurately identified Parkinson’s patients 87.7% of the time and exhibited high sensitivity in detecting individuals at risk of developing Parkinson’s.
This study stands as the largest conducted to date. Researchers suggest that this study could revolutionize Parkinson’s diagnosis, research, and treatment trials. Nonetheless, larger-scale studies are necessary. Researchers hold optimism that, in the future, the test will be conducted using blood samples instead of spinal fluid.
Treatment
Parkinson’s is not curable, but medications can dramatically and often effectively control its symptoms. Surgery may be recommended in certain cases.
You might also receive advice to incorporate lifestyle changes, such as engaging in aerobic exercise. Physical therapy that focuses on enhancing balance and flexibility can play a crucial role in specific situations. Additionally, a speech-language pathologist might assist in addressing speech-related issues.
Medication
You can use medication to manage issues with movement, walking, and tremors. These medications either increase dopamine levels or replace them.
Individuals with Parkinson’s disease have low levels of dopamine in the brain. However, dopamine cannot be directly administered to the brain due to its inability to cross the blood-brain barrier.
Treatment for Parkinson’s can result in a significant improvement in your symptoms. However, over time, the effectiveness of medications often diminishes or becomes less consistent. In most cases, symptoms can still be well-controlled.
Medicines your care team may prescribe include:
- Carbidopa/Levodopa
Levodopa and carbidopa are combined (marketed as Lodosyn) to protect levodopa from early conversion into dopamine outside of the brain. This reduction in conversion helps to alleviate or prevent nausea.
Orthostatic hypotension is a condition that leads to nausea and lightheadedness.
The benefits of levodopa might decrease over time as your condition advances. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as “wearing off”.
Additionally, you might experience dyskinesia, which involves uncontrollable movements, particularly after taking high doses of levodopa. To manage these side effects, your healthcare team might consider lowering your dose or adjusting the timing of your doses.
For individuals with Parkinson’s disease, it’s advisable to take carbidopa and levodopa on an empty stomach.

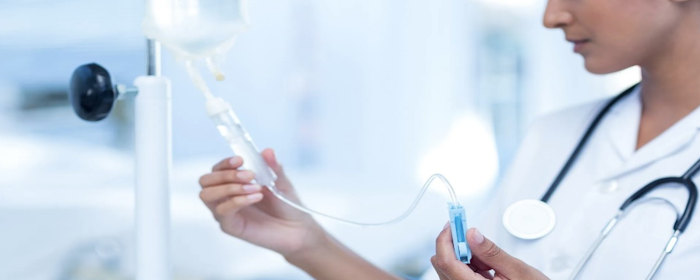
- Carbidopa and levodopa can be administered via inhalation.
The brand-name medication Inbrija is designed to deliver carbidopa and levodopa through this method. This medication is intended to help manage symptoms in cases where the effectiveness of oral medications suddenly diminishes.
- Another formulation, Carbidopa/levodopa Infusion
Sold under the brand name Duopa, combines carbidopa with levodopa. It is administered through a feeding tube, which delivers the gel-like medication directly to the small intestine.
Duopa can be prescribed to patients with advanced Parkinson’s disease who respond well to carbidopa and levodopa but experience fluctuations in their response. The continuous infusion of Duopa ensures a steady level of both medicines in the bloodstream. Placement of the tube requires a minor surgical procedure. Potential risks associated with the tube include infection at the infusion site or the tube becoming dislodged.
Schedule an Appointment at Stemedix Now
If you’re interested in exploring Parkinson’s Disease, we invite you to schedule an appointment with the experts at Stemedix. Our team of specialized medical professionals can help assess your needs and recommend a customized treatment plan to help improve your quality of life. Don’t wait to take control of your health – contact us today to schedule your appointment and begin your journey towards wellness.
Discover our wide range of treatments by calling us at (800) 531-0831













 St. Petersburg, Florida
St. Petersburg, Florida
